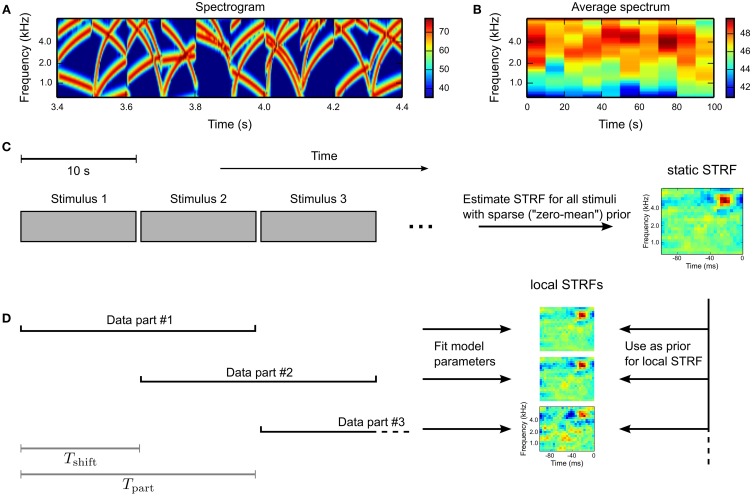
Figure 4.
Experimental design. Single units in the inferior colliculus (IC) and the primary auditory cortex (A1) in anesthetized Mongolian gerbils were probed with a dynamically fluctuating stimulus ensemble. Acoustic stimuli were composed of random frequency-modulated (FM) tone complexes arranged in 100 ms blocks. The stimulus sequence was interleaved every 10 s by a period of silence (100–1000 ms). (A) The spectrogram for a 1 s example. Amplitude values are given in decibel. (B) Average spectra for 10 s stimuli indicating stationary characteristics on medium and long time scales. Note the smaller range of amplitude values compared to (A). (C) For every unit, an STRF was estimated using the whole stimulus sequence and a GLM with zero-mean prior. Silence periods were not included in the analysis. (D) A time-varying STRF was constructed by subdividing the whole stimulus sequence in overlapping parts of length Tpart and temporal shift Tshift. For every part, a local STRF was estimated using a GLM with mixed prior (using the static STRF), yielding a sequence of time-varying STRFs.