Figure 8.
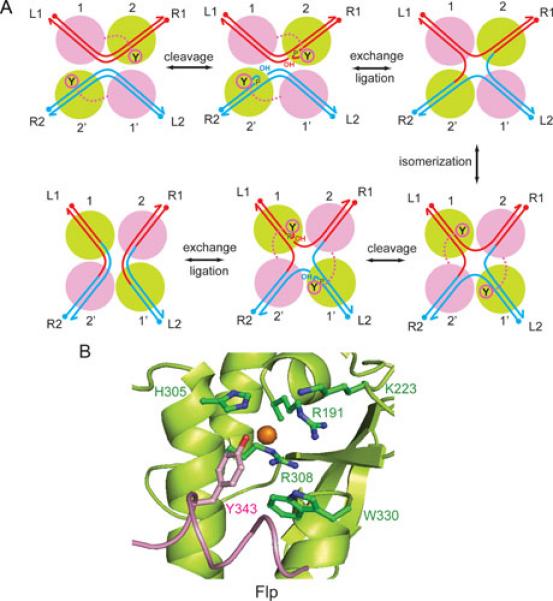
Flp mediated site-specific recombination. A. The recombination reaction is initiated by the synapsis of two FRT sites L1-R1 and L2-R2; L = left; R = right), each bound by two monomers of Flp (1, 2; 1’, 2’) across from the strand exchange region. The antiparallel arrangement of sites (left to right at the top and right to left at the bottom) within the recombination synapse is consistent with most (but not all) published data. The first pair of strand cleavage-exchange reactions gives rise to a Holliday junction intermediate; the second pair of analogous reactions resolves the junction into recombinant products, L1-R2 and L2-R1. The active Flp monomers, those adjacent to the scissile phosphates that are targeted by the active site tyrosine nucleophiles during a cleavage-exchange step, are shown in green. The switch between the active and inactive (magenta) pairs of Flp monomers accompanies the isomerization of the Holliday junction intermediate. B. The organization of key catalytic residues within the Flp active site is shown (75, 89). The conserved catalytic pentad of the tyrosine family corresponds to Arg-191, Lys-223, His-305, Arg-308 and Trp-330 in Flp. The active site tyrosine (Tyr-343) is delivered by a second Flp monomer.
