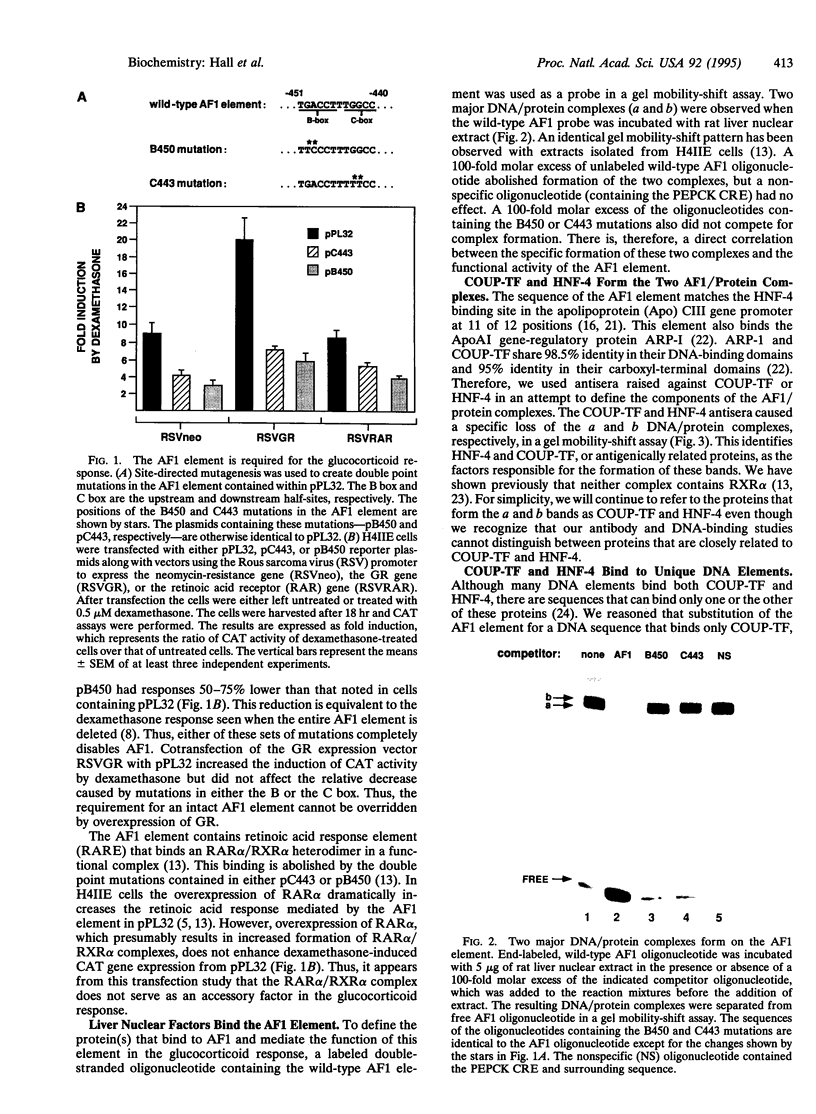
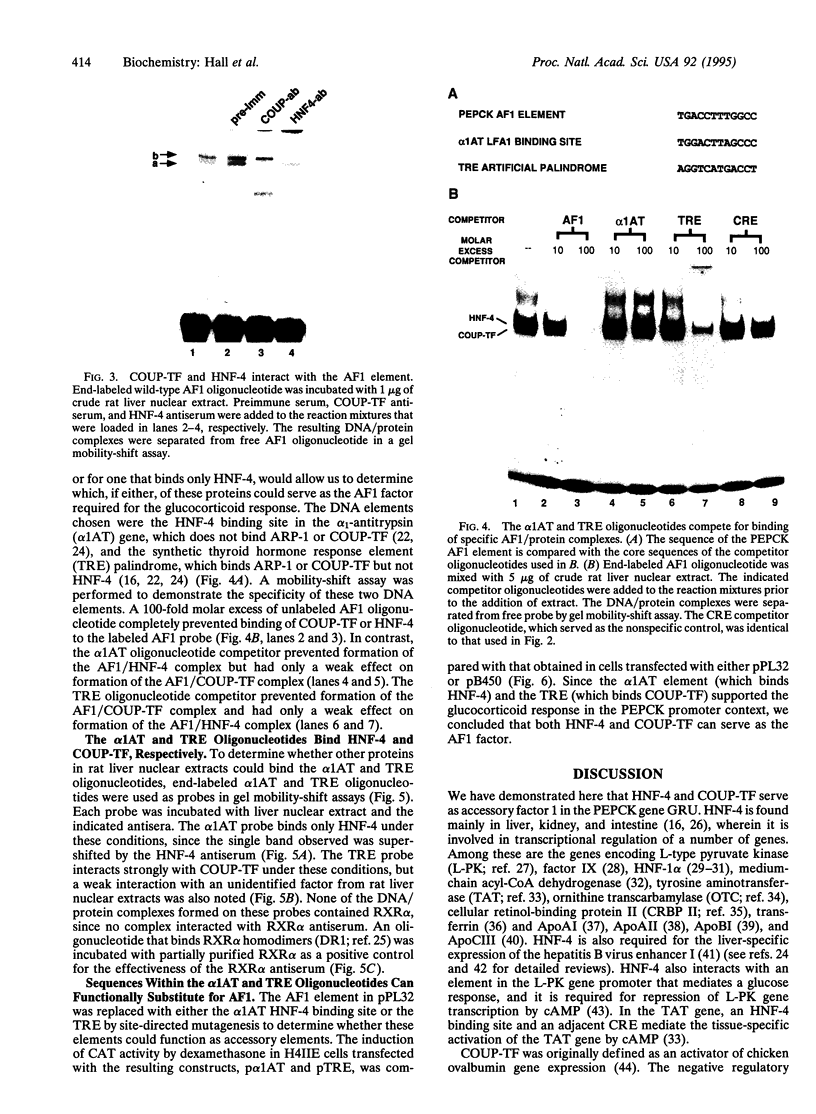
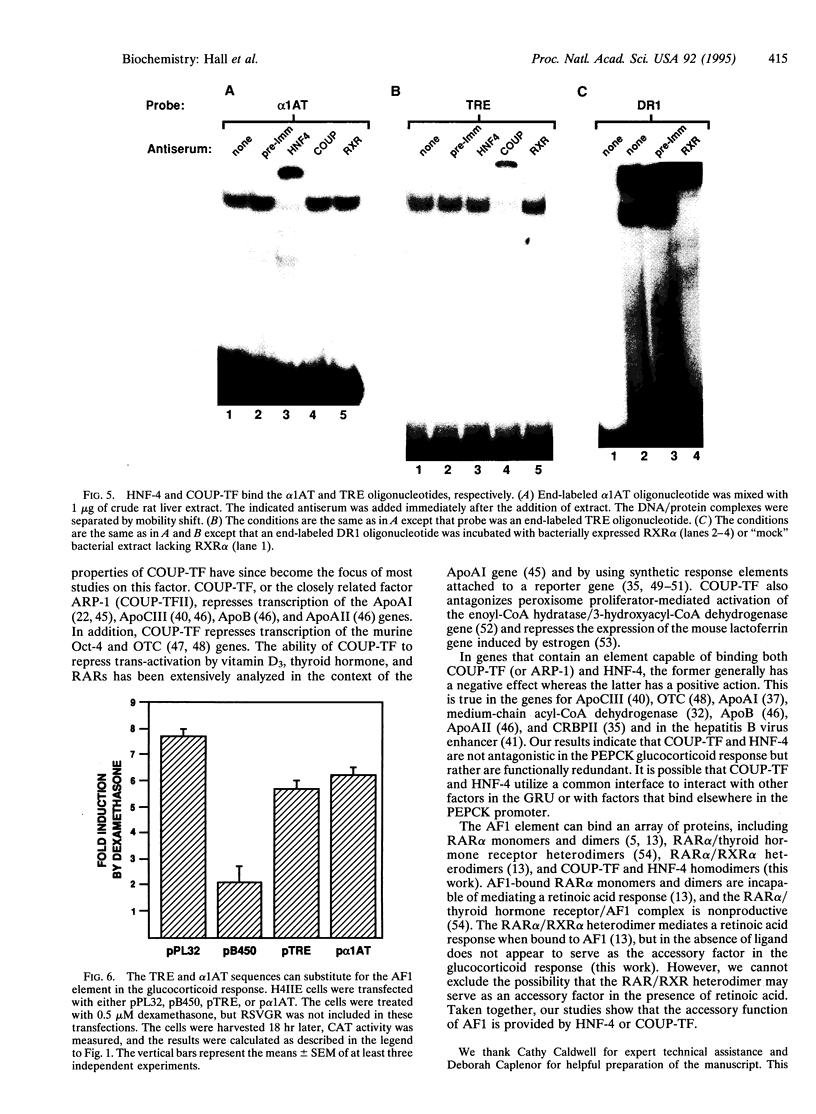
Abstract
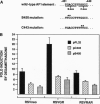
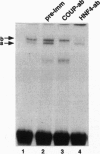
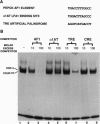
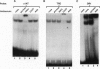
Glucocorticoids stimulate hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK; EC 4.1.1.32) gene expression, thereby increasing the rate of gluconeogenesis. The effect of glucocorticoids on PEPCK gene expression is mediated by a set of promoter elements collectively referred to as the glucocorticoid response unit. The response unit spans a 100-bp segment and includes two glucocorticoid receptor binding sites (GR1 and GR2) and two accessory factor binding sites (AF1 and AF2), all of which are required for a maximal glucocorticoid response. The AF1 element also serves as a retinoic acid response element and may be involved in developmental and tissue-specific expression of the gene. In this study we report that COUP-TF and HNF-4, two orphan members of the nuclear receptor superfamily, bind to the AF1 element and function as accessory factors for the glucocorticoid response of the PEPCK gene.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cardot P., Chambaz J., Kardassis D., Cladaras C., Zannis V. I. Factors participating in the liver-specific expression of the human apolipoprotein A-II gene and their significance for transcription. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):9080–9093. doi: 10.1021/bi00086a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. E., Gulick T., Raisher B. D., Caira T., Ladias J. A., Moore D. D., Kelly D. P. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 activates medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene transcription by interacting with a complex regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13805–13810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Nakabayashi H., Wong N. C. HNF-4 increases activity of the rat Apo A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1205–1211. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. T., Granner D. K. The effect of phorbol esters and diacylglycerol on expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene in rat hepatoma H4IIE cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16848–16853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Leng X., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Multiple mechanisms of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor-dependent repression of transactivation by the vitamin D, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4152–4160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4153–4163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuif M. H., Cognet M., Boquet D., Tremp G., Kahn A., Vaulont S. Elements responsible for hormonal control and tissue specificity of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4852–4861. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberger C. L., Nechushtan H., Cohen H., Shani M., Reshef L. Differential regulation of the rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression in several tissues of transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1396–1403. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Casanova J., Raaka B. M., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. Half-site spacing and orientation determines whether thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors and related factors bind to DNA response elements as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):429–442. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. D., Ostapchuk P., Hearing P. Functional interaction of nuclear factors EF-C, HNF-4, and RXR alpha with hepatitis B virus enhancer I. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3940–3950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3940-3950.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Andreone T., Sasaki K., Beale E. Inhibition of transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by insulin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):549–551. doi: 10.1038/305549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., O'Brien R., Imai E., Forest C., Mitchell J., Lucas P. Complex hormone response unit regulating transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene: from metabolic pathways to molecular biology. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:319–348. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Pilkis S. The genes of hepatic glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10173–10176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. A., Kessler M., Lynch G. Kainate binding to the AMPA receptor in rat brain. Neurochem Res. 1994 Jun;19(6):777–782. doi: 10.1007/BF00967719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. K., Scott D. K., Noisin E. L., Lucas P. C., Granner D. K. Activation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene retinoic acid response element is dependent on a retinoic acid receptor/coregulator complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5527–5535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Miner J. N., Mitchell J. A., Yamamoto K. R., Granner D. K. Glucocorticoid receptor-cAMP response element-binding protein interaction and the response of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene to glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5353–5356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Stromstedt P. E., Quinn P. G., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Granner D. K. Characterization of a complex glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4712–4719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Nishiyori A., Murakami T., Tsukamoto T., Hata S., Osumi T., Okamura R., Mori M., Takiguchi M. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor (COUP-TF) represses transcription from the promoter of the gene for ornithine transcarbamylase in a manner antagonistic to hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 (HNF-4). J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11125–11133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Chen L., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Crabtree G. R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):457–461. doi: 10.1038/355457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Kardassis D., Cardot P., Cheng J., Zannis V., Cladaras C. Transcriptional regulation of human apolipoprotein genes ApoB, ApoCIII, and ApoAII by members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily HNF-4, ARP-1, EAR-2, and EAR-3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15849–15860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Reue K., Melian A., Culver H., Breslow J. L. A regulatory element in the ApoCIII promoter that directs hepatic specific transcription binds to proteins in expressing and nonexpressing cell types. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16132–16137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Yang N., Teng C. T. COUP-TF acts as a competitive repressor for estrogen receptor-mediated activation of the mouse lactoferrin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1836–1846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., Forman B. M., Samuels H. H., Granner D. K. Specificity of a retinoic acid response element in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter: consequences of both retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5164–5170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., O'Brien R. M., Mitchell J. A., Davis C. M., Imai E., Forman B. M., Samuels H. H., Granner D. K. A retinoic acid response element is part of a pleiotropic domain in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Chen J. Y., Chen Z., White J., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. The patterns of binding of RAR, RXR and TR homo- and heterodimers to direct repeats are dictated by the binding specificites of the DNA binding domains. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5029–5041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrane M. M., Yun J. S., Patel Y. M., Hanson R. W. Metabolic control of gene expression: in vivo studies with transgenic mice. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90426-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Halaas J. L., Breslow J. L., Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and bZip protein C/EBP alpha bind to overlapping regions of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16831–16838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietus-Snyder M., Sladek F. M., Ginsburg G. S., Kuo C. F., Ladias J. A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Karathanasis S. K. Antagonism between apolipoprotein AI regulatory protein 1, Ear3/COUP-TF, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 modulates apolipoprotein CIII gene expression in liver and intestinal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1708–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Noisin E., Hall R., O'Brien R., Imai E., Granner D. Integration of multiple signals through a complex hormone response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 May;8(5):585–594. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.5.8058068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Tanaka K. Analysis of the rat hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 1 gene promoter: synergistic activation by HNF4 and HNF1 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3731–3736. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata K. S., Zhang B., Marcus S. L., Capone J. P., Rachubinski R. A. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) binds to a peroxisome proliferator-responsive element and antagonizes peroxisome proliferator-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19169–19172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakshatri H., Chambon P. The directly repeated RG(G/T)TCA motifs of the rat and mouse cellular retinol-binding protein II genes are promiscuous binding sites for RAR, RXR, HNF-4, and ARP-1 homo- and heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):890–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyori A., Tashiro H., Kimura A., Akagi K., Yamamura K., Mori M., Takiguchi M. Determination of tissue specificity of the enhancer by combinatorial operation of tissue-enriched transcription factors. Both HNF-4 and C/EBP beta are required for liver-specific activity of the ornithine transcarbamylase enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1323–1331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Activation of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene is dependent on synergy between liver-specific and hormone-responsive elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5479–5483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Green P. P., 3rd, Fowlkes D. M. A rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):173–178. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. D., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Location and characterization of two widely separated glucocorticoid response elements in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos I., Zakin M. M. Transferrin gene as a model for liver-specific gene expression. Biol Cell. 1993;77(1):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(05)80175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Granner D. K. Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:885–909. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.004321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnen M. J., Sladek F. M., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. Disruption of a binding site for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 results in hemophilia B Leyden. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6300–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagami I., Tsai S. Y., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of two factors required for transcription of the ovalbumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4259–4267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoorlemmer J., van Puijenbroek A., van Den Eijnden M., Jonk L., Pals C., Kruijer W. Characterization of a negative retinoic acid response element in the murine Oct4 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1122–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Clouthier D. E., Schaefer I. M., Hammer R. E., Magnuson M. A., Beale E. G. Tissue-specific, developmental, hormonal, and dietary regulation of rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-human growth hormone fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1007–1020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and liver-specific gene expression. Receptor. 1993 Fall;3(3):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian J. M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific expression of the gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 may involve hepatocyte nuclear factor 4. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2225–2234. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran P., Zhang X. K., Salbert G., Hermann T., Lehmann J. M., Pfahl M. COUP orphan receptors are negative regulators of retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4666–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Kahn A. Transcriptional control of metabolic regulation genes by carbohydrates. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):28–35. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom R. L., Rhee M., Karathanasis S. K. Repression by ARP-1 sensitizes apolipoprotein AI gene responsiveness to RXR alpha and retinoic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3380–3389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Prezioso V. R., Chen W. S., Sladek F. M., Cortese R., Darnell J. E., Jr The different tissue transcription patterns of genes for HNF-1, C/EBP, HNF-3, and HNF-4, protein factors that govern liver-specific transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3807–3811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]