Figure 4.
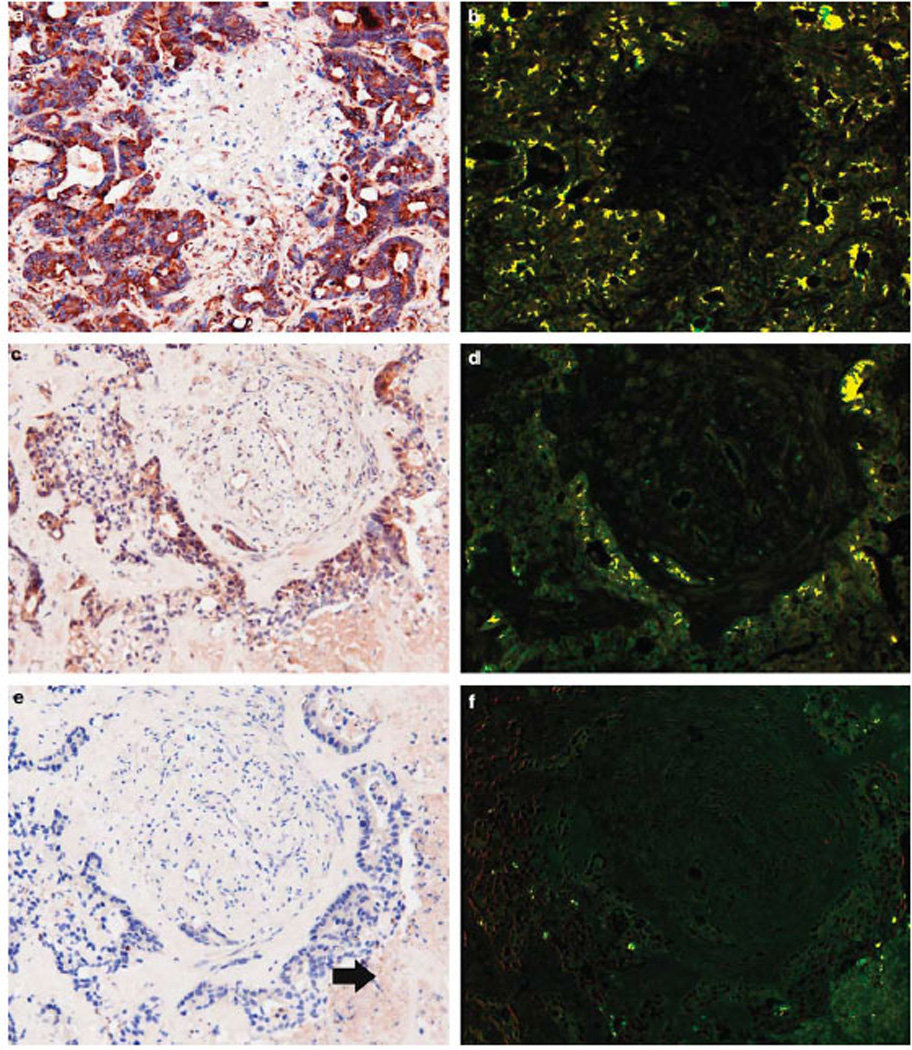
Molecular correlates of reoviral infection in serial tissue sections. Serial sections from a metastatic colon cancer from a patient treated with reovirus were analyzed for co-expression of reovirus and tubulin (a), reovirus and p38 (c), plus reovirus and caspase-3 (e); note the small area of apoptosis (arrow). The images were then analyzed with the Nuance system to assess the degree of co-expression; reoviral protein is fluorescent red and the cellular protein fluorescent green. There is extensive co-expression of reoviral and tubulin protein (b, seen as fluorescent yellow), indicative of productive infection. Similarly, reoviral and p38 proteins are often detected in the same cells (d); note that the co-expression is evident only in cancer cells and not in the surrounding stromal cells. Co-expression analyses between reovirus and caspase-3 showed rare cells positive for both proteins in the area of apoptosis (f).
