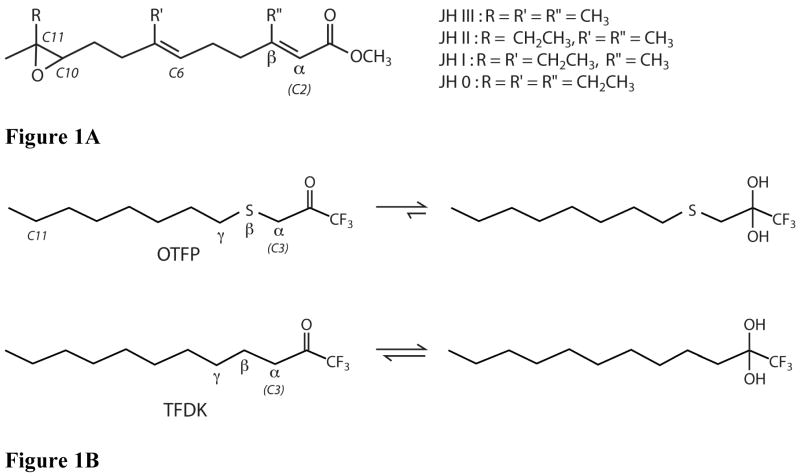
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of JHE substrates and inhibitors of JHE. A) Structure of JH 0, I, II, and III. For all JH’s, both unsaturated bonds are in the E isomeric form. All JH’s have a chiral center at carbon 10, and this is the R isomer for all. In addition, JH 0, I, and II have a chiral center at carbon 11. For all three, this is the S isomer. B) Structures of OTFP and TFDK. In aqueous solution the ketone to gem-diol equilibrium is shifted towards the diol based upon inhibitor potency, with potent inhibitors (e.g. OTFP) favoring the gem-diol form. The Greek letters α, β and γ refer to atom position relative to the carbonyl carbon.