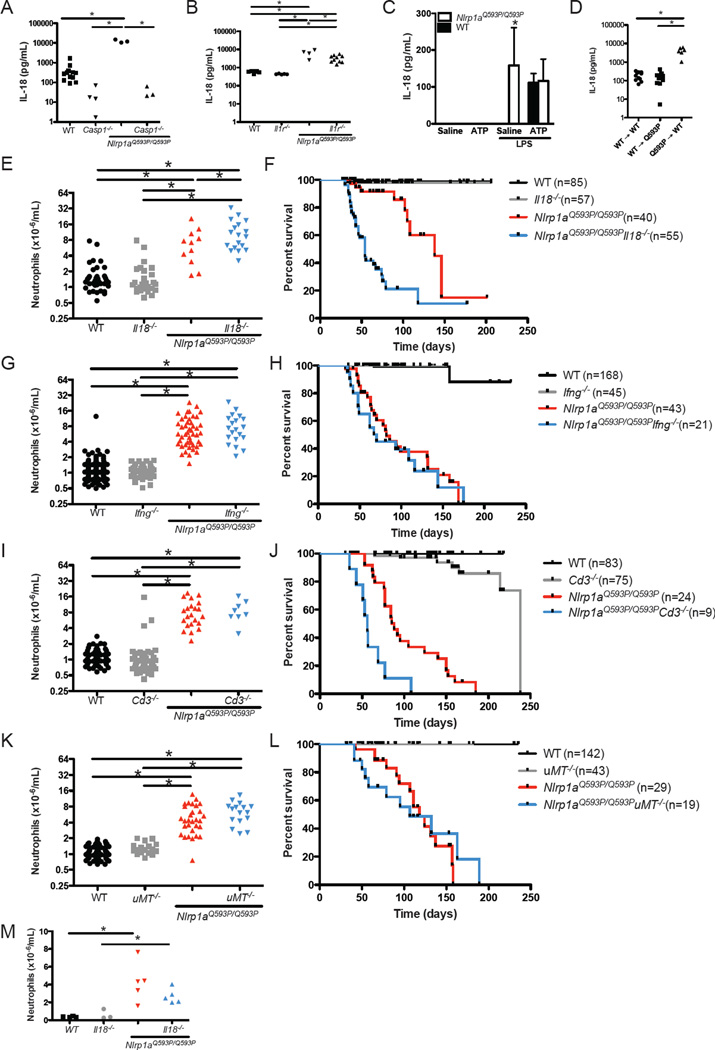
Figure 3. IL-18 inhibits the lethal multiorgan inflammatory disease in Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice.
(A, B) Serum IL-18 was measured by ELISA in wild-type, Casp1−/−, Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P, Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P Casp1−/−, Il1r−/− and Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P Il1r−/− mice. (C) IL-18 production by Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P macrophages following stimulation with 2 ng/mL LPS and 5mM ATP. (D) Serum IL-18 levels in lethally-irradiated mice after reconstitution with Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P or wild-type bone marrow cells. (E–L) Neutrophil numbers in the peripheral blood of Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice lacking IL-18 (E), IFNγ (G), T cells (I) or B cells (K). Survival of Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice lacking IL-18 (F), IFNγ (H), T cells (J) or B cells (L). A significant change (p<0.05) in disease-free survival is evident between Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P Il18−/− and Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice, as well as between Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P Cd3−/− and Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice. (M) Neutrophil numbers in the peripheral blood of germ-free Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P Il18−/− and Nlrp1aQ593P/Q593P mice. *p<0.05.