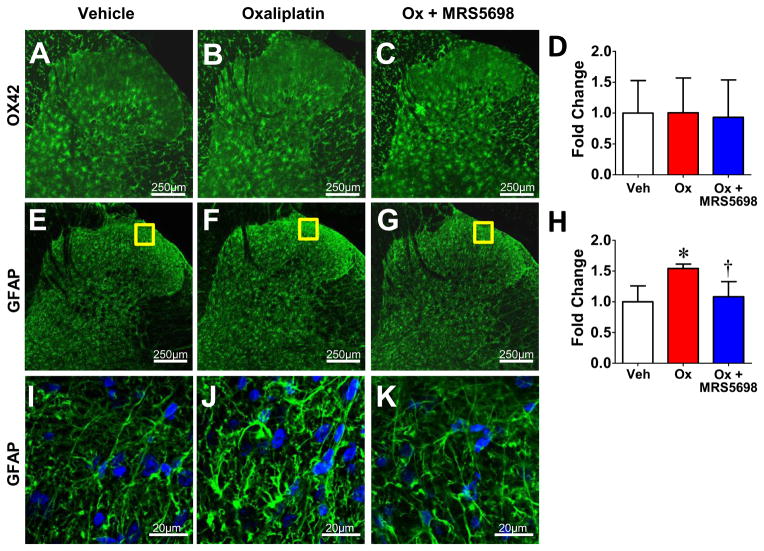
Fig. 4. MRS5698 prevents spinal astrocytic hyperactivation after oxaliplatin treatment.
When compared to vehicle (A), oxaliplatin treated rats (B) at day 25 demonstrated no change in immunolabeling for OX42 (green) bilaterally within the superficial dorsal horn (i.e., laminae I and II) with (C) or without (B) MRS5698 treatment. When compared to vehicle (E), oxaliplatin treated rats at D25 (F) demonstrated enhanced immunolabeling for GFAP (green) bilaterally within the superficial dorsal horn. The A3AR agonist MRS5698 blocked enhanced GFAP immunostaining (G). Negative controls exhibited low levels of background fluorescence. Micrographs are from the L4 level and represent n=4 animals per group (3 sections per animal from L4, L5, and L6). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was normalized to vehicle and expressed as fold change for OX42 (D) and GFAP (H). I–K: Higher magnification representative images. Results are expressed as mean ± SD and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s comparisons. *P<0.05 Oxaliplatin vs. Vehicle; †P<0.05 Ox+MRS5698 vs. Oxaliplatin.