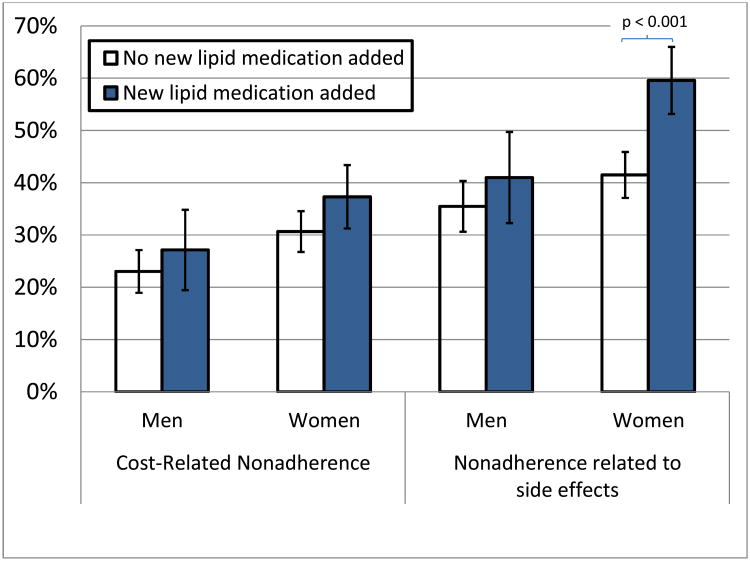
Figure 1.
Comparing the association of treatment intensification with patient-reported cost-related nonadherence and nonadherence related to side-effects of the medication across genders. After adjustment for age, education, race/ethnicity and insurance status, the test for gender by regimen intensification interaction is significant for nonadherence related to side effects (p=0.048). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.