Fig. 1.
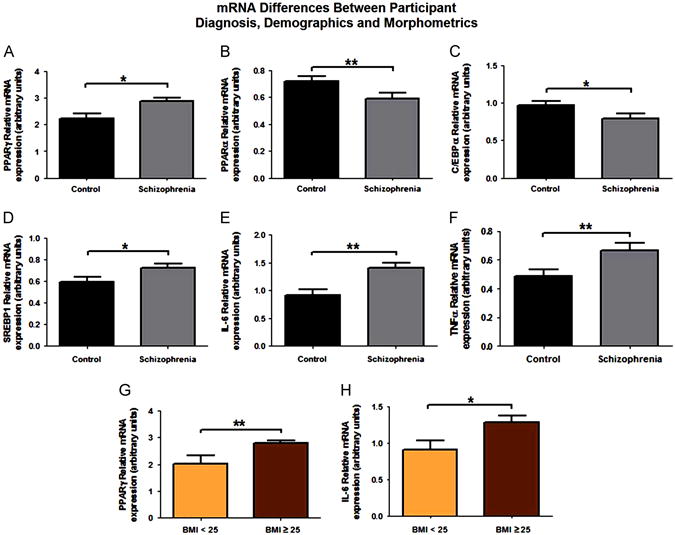
Diagnosis, demographics and morphometrics of obesogenic and immunogenic genes. Significant results are obtained from multiple regressions with each gene of interest as the dependent variable and diagnosis, medication use (in CPZ units), age, BMI, sex, a previous diagnosis of diabetes, age of onset of psychotic symptoms and tobacco consumption as explanatory variables. (A) Increased PPARγ mRNA levels were seen in patients with schizophrenia when compared to normal controls. Patients with schizophrenia had significantly decreased levels of both PPARα (B) and C/EBPα (C) mRNA when compared to normal controls. Increased SREBP1 (D), IL-6 (E) and TNFα (F) mRNA levels were seen in patients with schizophrenia when compared to their normal control counterparts. PPARγ and IL-6 mRNA were also significantly increased in overweight participants (BMI≥25), as determined by multiple linear regression. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
