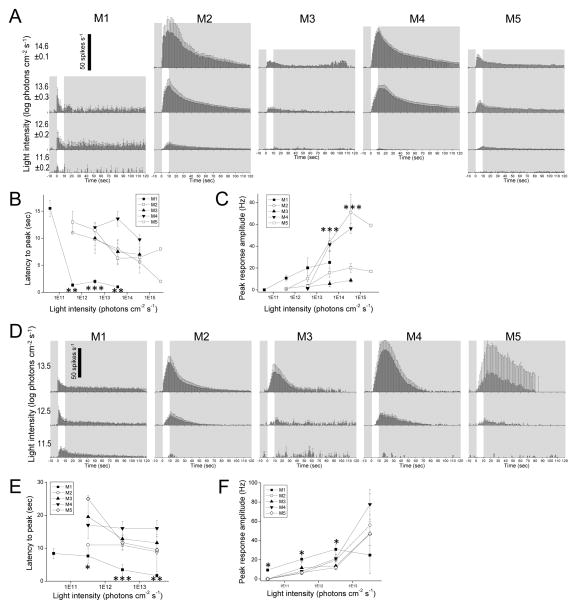
Figure 5. Melanopsin-driven spiking responses to light.
The intrinsic photoresponses of rat ipRGCs (A – C) are compared with those of mouse ipRGCs from Zhao et al. 2014 (D – F). A,D) Averaged spike histograms with 1-sec bin width. All stimuli were 10-sec light steps that started at time = 0, and are represented by the white regions. B,E) Averaged latencies to peak. The asterisks highlight the M1 data that were significantly different from those of the other cells. C,F) Averaged peak amplitudes. In C, M2 and M4 were significantly different from the other cell types at the asterisked light intensities. In F, M1 was significantly different from the other cells at the asterisked intensities. N values for the rat data: M1, 2 – 4; M2, 3 – 7; M3, 1 – 3; M4, 8 – 12; M5, 2 – 8. N values for the mouse data: M1, 4 – 10; M2, 10 – 14; M3, 5 – 7; M4, 4 – 9; M5, 2 – 4.