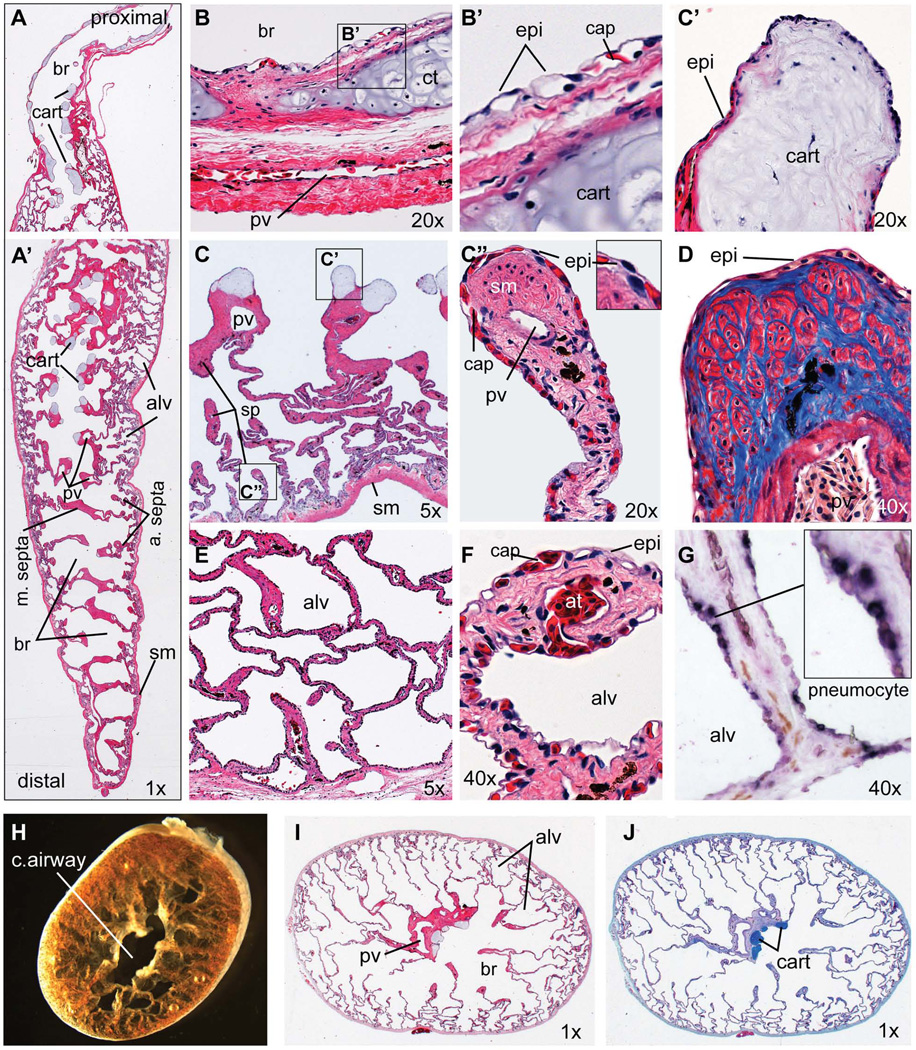
Figure 2. Histology of the adult Xenopus laevis lung.
(A–G) Longitudinal sections of an adult Xenopus laevis lung including (A) the proximal and (A’) distal regions. (B) 20X view of proximal main bronchi showing the epithelial lining and bronchi walls with cartilage plate surrounded by layers of smooth muscle and connective tissue containing a major blood vessel. (B’) Detail view of boxed area in (B) showing the epithelial cells in close apposition to capillaries. (C) 5X view of the proximal lung showing major septa containing a pulmonary vein and terminal cartilage nodules with smaller septa forming alveoli. (C’) 20X view of a cartilage nodule at the end of the major septa. (C”) 20X view showing the tip of an alveolar septa. (D) 40X view of an alveolar septa tip stained with Mason’s Trichrome showing collagen fibers (blue) and muscle fibers (red). (E) 5X view of smaller alveoli at the lung periphery. (F) 40X view of the blood-air interface in the small alveolar walls. (G) In-situ hybridization of sftpc (dark purple staining) showing expression in epithelial pneumocytes. (H) Brightfield of the adult Xenopus lung (distal portion) cut in a transverse plane immediately after dissection. (I) H&E-stained and (J) Alcian blue-stained transverse sections Abbreviations: alv, alveolar space; at, arteriole; br, bronchiolar space; cap, capillary; cart, cartilage; epi, epithelial cell; pv, pulmonary vein; sm, smooth muscle; sp, septae.