Fig. 1.
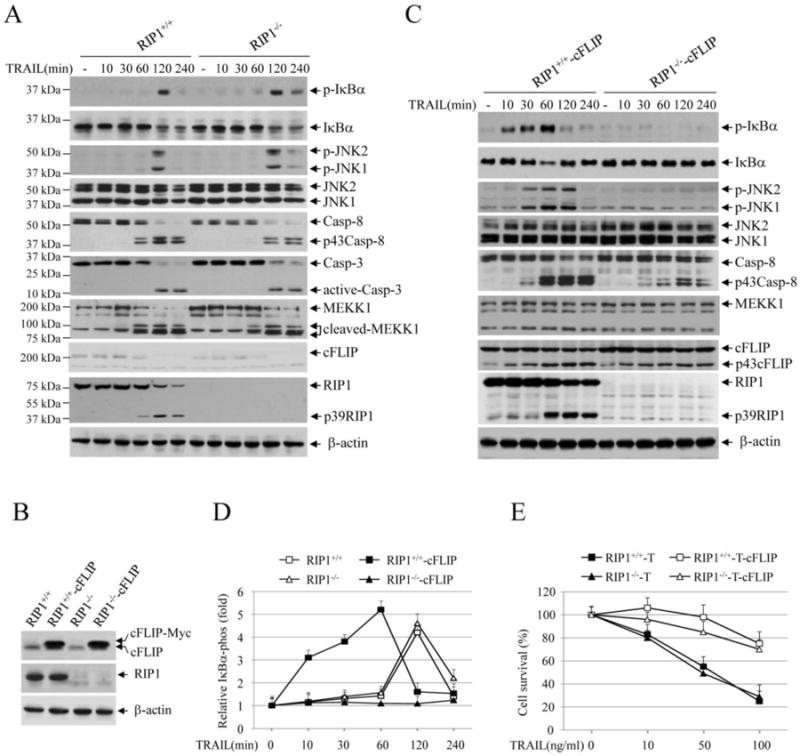
TRAIL induces IKK and JNK activation through RIP1-dependent and -independent pathways. (A) RIP1+/+ and RIP1-/- Jurkat T cells were treated with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) as indicated, and phosphorylation of IκBα and JNK, cleavage of caspase-8/3, MEKK1, cFLIP and RIP1 were examined by Western blotting. (B) RIP1+/+ and RIP1-/- Jurkat T cells were stably transduced with pBabe-puro-cFLIP (RIP1+/+-cFLIP and RIP1-/- -cFLIP), and the expression of cFLIP was then confirmed by Western blotting. (C) RIP1+/+-cFLIP and RIP1-/- -cFLIP Jurkat T cells were treated with TRAIL, and the activation of the downstream pathways was analyzed by Western blotting as in A. (D) IκBα phosphorylation blots from RIP1+/+, RIP1-/-, RIP1+/+-cFLIP and RIP1-/- -cFLIP Jurkat T cells treated with or without TRAIL was quantified by densitometry, and the ratios of IκBα phospho-signal over non-phospho-signal were normalized to 0 min signal. The relative values from three independent experiments were then presented as mean ± SE. (E) RIP1+/+, RIP1-/-, RIP1+/+-cFLIP and RIP1-/- -cFLIP Jurkat T cells were treated with TRAIL as indicated, and 24 hours after treatment, cell viability was assessed by MTT assays. Data shown are the mean ± SE of three experiments.
