Fig. 6.
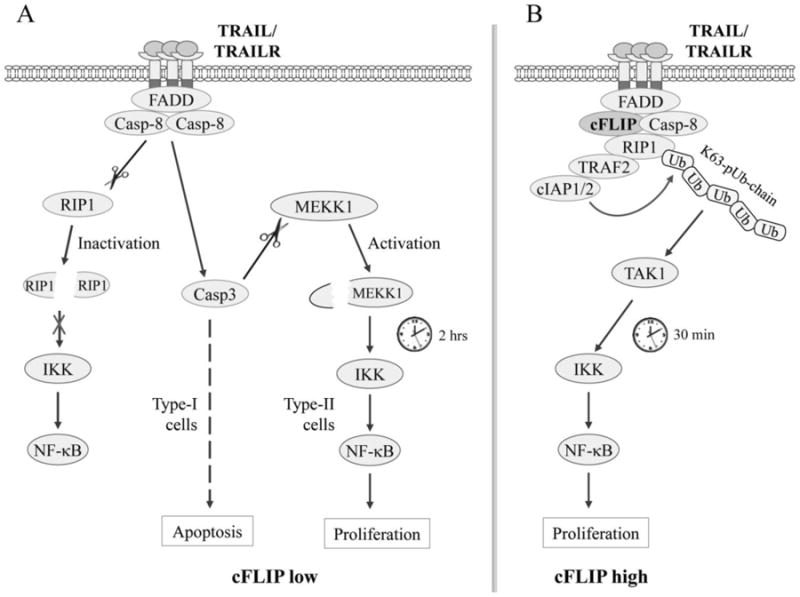
The TRAIL signaling pathways to NF-κB activation in apoptosis-sensitive and -resistant cells. (A) In cells with low cFLIP expression, ligation of TRAILR leads to its recruitment and activation of caspase-8 via FADD, which in turn cleaves RIP1 and impairs RIP1-dependent immediate IKK/NF-κB activation. Simultaneously, caspase-8 cleaves and activates caspase-3, which in turn activates MEKK1 by cleaving its regulatory domain, resulting in MEKK1-dependent activation of IKK/NF-κB at a later time. In Type-I cells, caspase-8-mediated caspase-3 activation is sufficient to trigger apoptosis, and thereby it disrupts MEKK1/IKK/NF-κB-dependent gene expression and cell proliferation, whereas in Type-II cells in which caspase-8-mediated caspase-3 activation is insufficient to trigger apoptosis, caspase-8/3-dependent MEKK1 and IKK/NF-κB activation is able to induce target gene expression and cell proliferation. (B) In cells with high cFLIP expression, cFLIP competes with caspase-8 for binding to FADD and thereby restricts its full activation, allowing the recruitment of RIP1, TRAF2 and cIAP1/2 to the TRAILR complex. TRAF2 and cIAP1/2 then catalyze RIP1 ubiquitination through K63-linkages, resulting in RIP1 ubiquitination-dependent immediate IKK/NF-κB activation.
