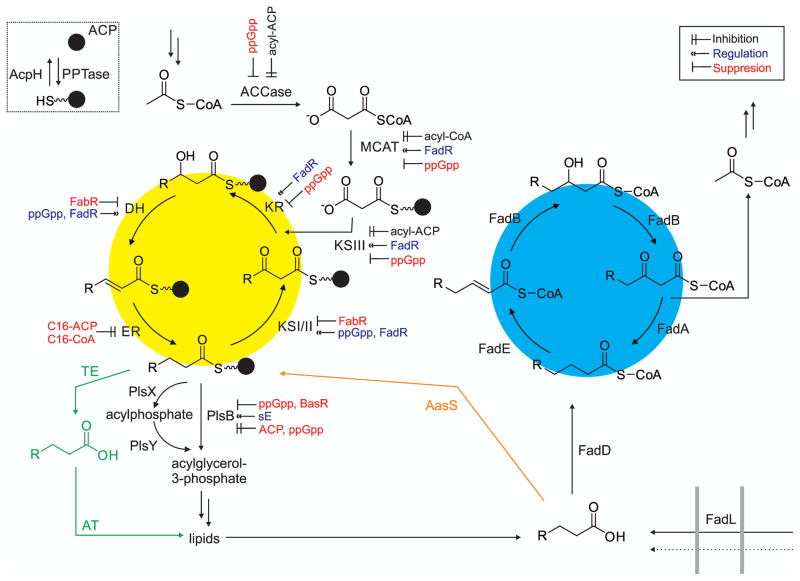
Figure 10.
Fatty acid metabolism in bacteria. In the fatty acid synthase (yellow circle): ACCase is the acetyl-CoA carboxylase; MCAT, malonyl-CoA acyltransferase; KSIII (FabH), ketoacyl synthase; KR (FabG), ketoreductase; DH (FabA/FabZ), dehydratase; ER (FabI/K/L/V), enoyl-ACP reductase; KSI (FabB), KSII (FabF), ketoacyl synthases and PlsB, acyltransferase. In green the thioesterase (TE) pathway present in plants, algae and some bacteria. In orange the acyl-ACP synthetase (AasS) found in some organisms. The dotted arrow in the bottom right corner represent diffusion of fatty acids into the cell, as well as active FadL-mediated transport. Fatty acid catabolism (blue circle): FadD, CoA-ligase; FadE, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; FadB, dual-function enoyl-CoA hydratase and hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; FadA, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase. FadR and FabR are the master regulators of fatty acid degradation and fatty acid biosynthesis, whereas ppGpp is an alarmone.