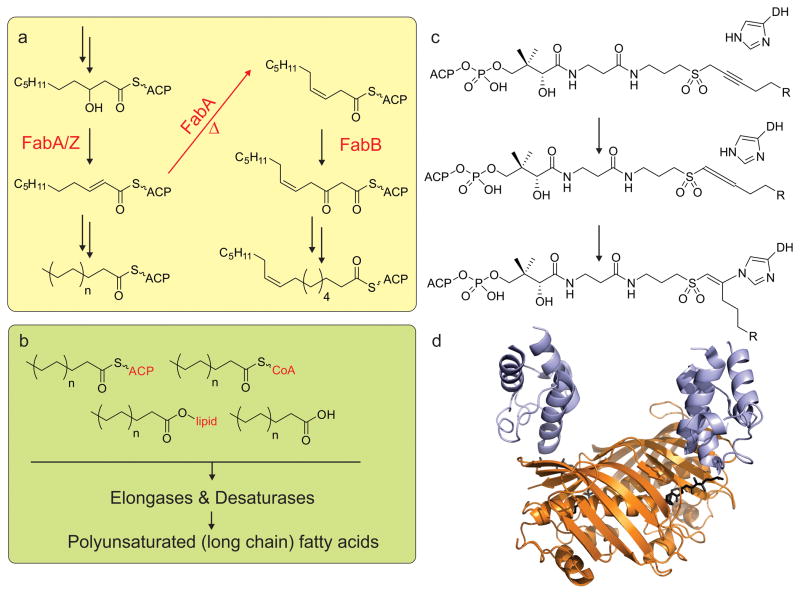
Figure 6.
Dehydratases. a) The bacterium E. coli has only one way to produce unsaturated fatty acids: FabA can not only reduce 3-hydroxydecanoyl-ACP, but also isomerize the double bond from trans-2-decenoyl-ACP to cis-3-decenoyl-ACP. Subsequent chain elongation by action of the other fatty acid synthase enzymes leads to the fatty acid C16:1. b) Other organisms (including cyanobacteria, plants, algae) have elongases and desaturases (green panel) that can extend and desaturate the saturated C16:0 or C18:0 fatty acids, as either acyl-ACP, acyl-CoA, acyl-lipid or free fatty acids. c) Mechanistic crosslinking between ACP and DH using a sulfonyl alkynyl pantetheinamide probe. d) The mechanistically crosslinked X-ray crystal structure of E. coli AcpP with FabA (PDB: 4KEH).