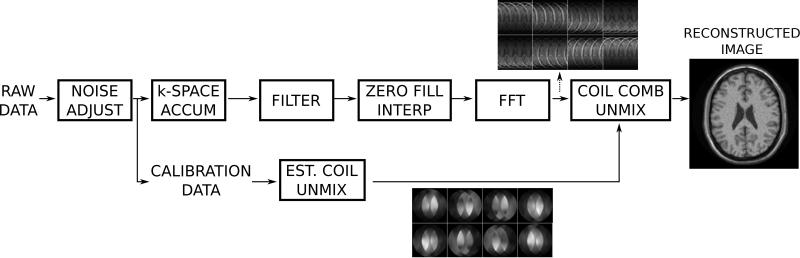
Figure 15.
Illustration of a typical reconstruction pipeline for a Cartesian parallel imaging acquisition. The first step in the reconstruction is noise pre-whitening (noise adjust), which removes noise correlation in the data. The data pipeline then splits into two, one for the main image reconstruction and one for the processing of calibration data to form parallel imaging unmixing coefficients. The main processing pipeline performs raw data filtering, zero filling in k-space to ensure square pixels (image interpolation), Fourier transform, and finally coil combination using the parallel imaging unmixing coefficients. This final step turns the aliased channel images into a single combined image.