FIGURE 6.
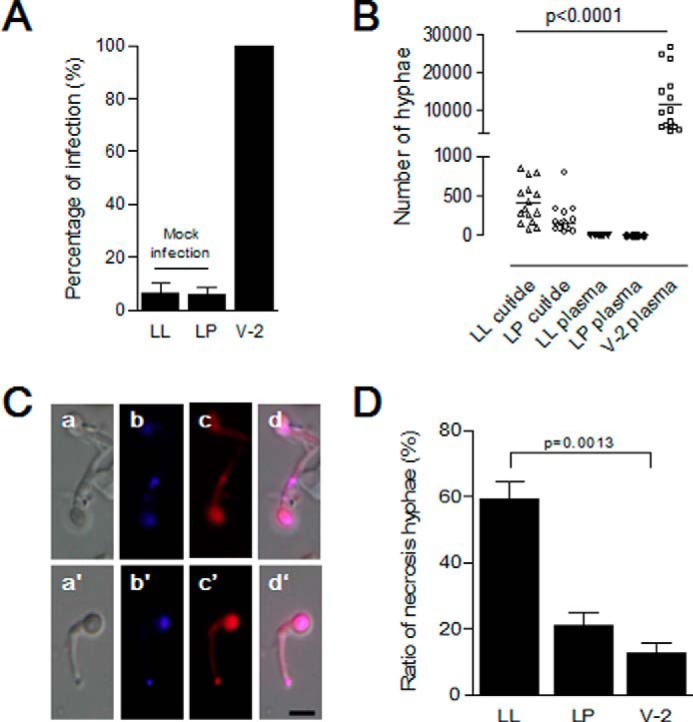
B. bassiana hyphae cannot penetrate the new cuticles of larvae undergoing ecdysis. Insect larvae undergoing the fourth larval-larval (LL) or larval-pupal (LP) ecdysis or feeding stage (V-2) were infected with B. bassiana conidia as in Fig. 5. A, percentages of infected larvae. Bars represent the means of three independent measurements ± S.E. (error bars) (15 individuals in each group). B, no hyphae were found in the hemolymph of larvae undergoing ecdysis. Hyphae on the insect surface and in molting fluids were suspended in buffer for counting after self-ecdysis or manual removal. Hyphae in hemolymph of all larvae were also counted after bleeding. Bars represent the mean of three independent measurements ± S.E. (error bars) (15 individuals in each group). C, morphology of fungal cells separated from molting fluids and cuticle surfaces. After suspension, hyphae were stained to detect living and dead cells, respectively (58, 59). Hyphae with strong red fluorescence were dead. a–d, hyphae from infected larvae (LL) as in Fig. 5A (a); a′–d′, hyphae from infected larvae (LP) as in Fig. 5K (a). d and d′, merged image using blue (b and b′) and red (c and c′) filters. D, percentages of dead hyphae as shown in C. For infected feeding larvae in V-2, hyphae washed from cuticle surfaces alone were assayed. Bars represent the means of three independent measurements ± S.E. (error bars) (15 individuals in each group). Scale bar, 5 μm.
