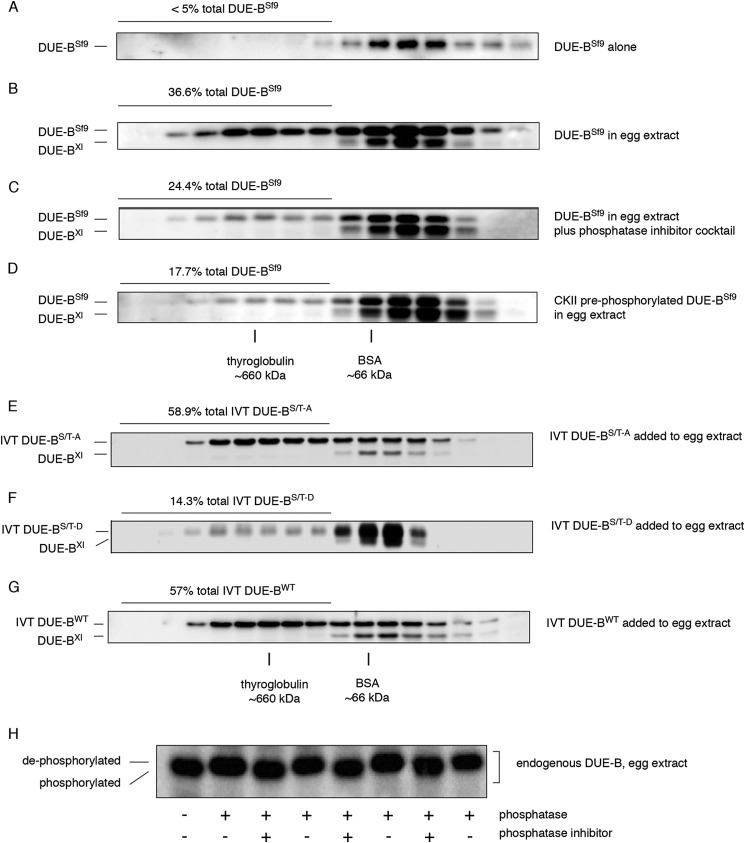
FIGURE 2.
Phosphorylation controls DUE-B incorporation into high molecular weight complexes. A, recombinant human DUE-B expressed and purified from Sf9 insect cells (DUE-BSf9) was fractionated by gel filtration. B, DUE-BSf9 was incubated with the interphase egg extract and fractionated by gel filtration. C, interphase egg extract was supplemented with phosphatase inhibitor mixture and incubated with DUE-BSf9. Proteins were separated by gel filtration. D, DUE-BSf9 was phosphorylated by casein kinase II prior to incubation with interphase egg extract. Proteins were separated using gel filtration after incubation. E, recombinant His6-tagged human DUE-B C-terminal (amino acids 160–209, see Fig. 5) (S/T)-A mutant (all C-terminal Ser and Thr residues mutated to Ala) was synthesized in vitro and incubated with interphase Xenopus egg extracts. F, recombinant His6-tagged human DUE-B C-terminal (amino acids 160–209, see Fig. 5) Ser/Thr-Asp mutant (all C-terminal Ser and Thr residues mutated to Asp) was synthesized in vitro and incubated with interphase Xenopus egg extracts. G, recombinant His6-tagged human DUE-BWT was synthesized in vitro and incubated with interphase Xenopus egg extracts. H, DUE-B from interphase egg extract was treated with λ-phosphatase with or without phosphatase inhibitor. Replicate samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot.