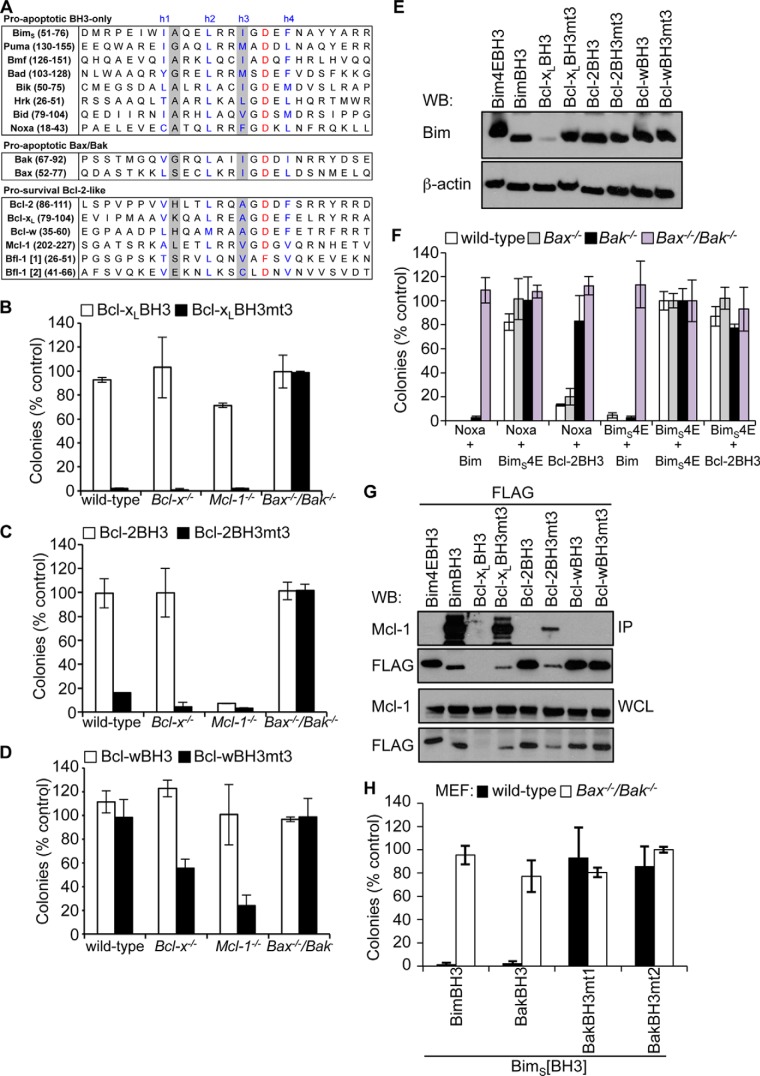
FIGURE 1.
Pro-survival BH3 domains bind pro-survival proteins poorly. A, alignment of BH3 domains from pro-apoptotic and pro-survival Bcl-2 family members. The four conserved hydrophobic residues h1–h4 are indicated (blue). Residues that distinguish pro-survival versus pro-apoptotic BH3 domains, h1 + 1 and h3, are shaded gray. Shown is killing activity of BimS chimeras with the Bcl-xL (B), Bcl-2 (C), or Bcl-w BH3 (D) domains and their h1 + 1/h3 (mt3) mutants in MEFs. E, Western blot showing relative expression of FLAG-tagged BimS and BimS chimeras expressed in Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs. F, killing activity of the Bcl-2 BH3 domain, BimS (positive control), or BimS4E (negative control) in MEFs co-expressing Noxa (to neutralize Mcl-1) or BimS4E as controls. Colonies were scored, and numbers were expressed as a percentage of the number observed in cells transduced with BimS4E alone. G, co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous Mcl-1 from Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs expressing FLAG-tagged BimS pro-survival BH3 chimeras. Western blots of immunoprecipitates (IP) and whole cell lysates (WCL) were probed with anti-Mcl-1 and anti-FLAG antibodies. H, BimS chimeras with mutant Bak BH3 domains fail to kill wild-type MEFs, unlike wild-type BimS or a chimera with the wild-type Bak BH3 sequence. Error bars, S.D. of n = 2–3 separate assays. In B–D, F, and H, colonies were scored 7 days after transduction, and numbers are expressed as a percentage of the number observed in cells transduced with an inert BimS mutant (BimS4E).