FIGURE 4.
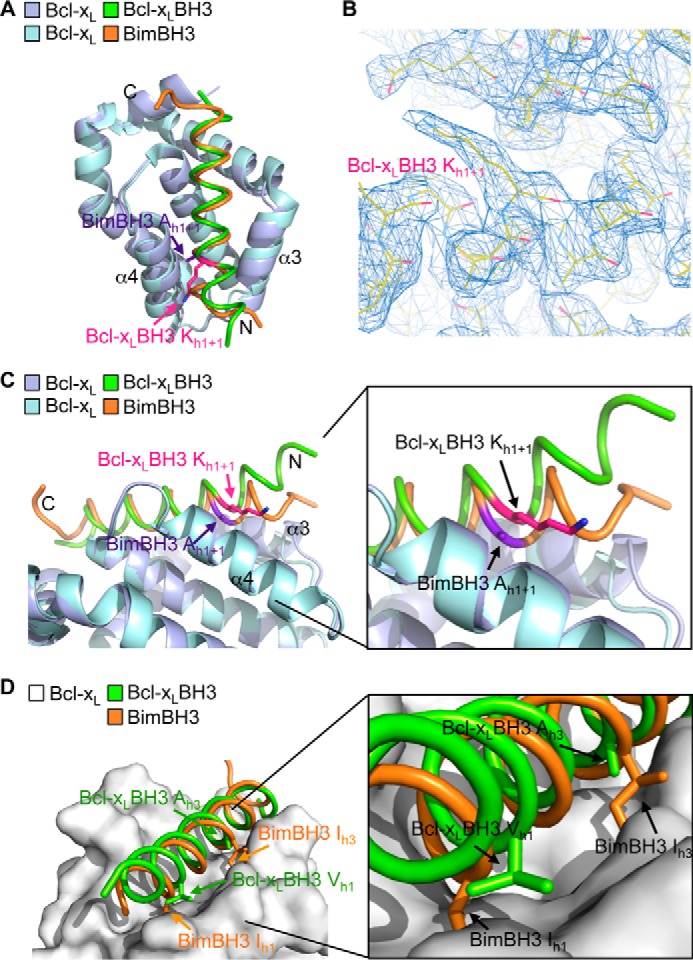
Crystal structure of Bcl-xL bound to its own BH3 domain. A, overlay of the crystal structures of Bcl-xL bound to its own BH3 domain (Bcl-xL molecule A (mauve) and Bcl-xL BH3 (green)) and bound to Bim BH3 (Bcl-xL (light blue) and Bim BH3 (orange)). B, region of the electron density map showing the lysine at h1 + 1 in the Bcl-xL BH3 peptide ligand. C, the N-terminal end of the Bcl-xL BH3 peptide ligand (green) is displaced out of the binding groove relative to the Bim BH3 domain (orange). D, the h1 hydrophobic residue in the Bcl-xL BH3 domain (green) is not buried in the binding groove, unlike the corresponding residue in Bim (orange). Similarly, hydrophobic contacts between Bcl-xL and the h3 residue of the Bcl-xL BH3 ligand are greatly reduced due to the small alanine residue here compared with the larger hydrophobic residue found in all pro-apoptotic BH3 domains (such as the isoleucine in Bim).
