FIGURE 8.
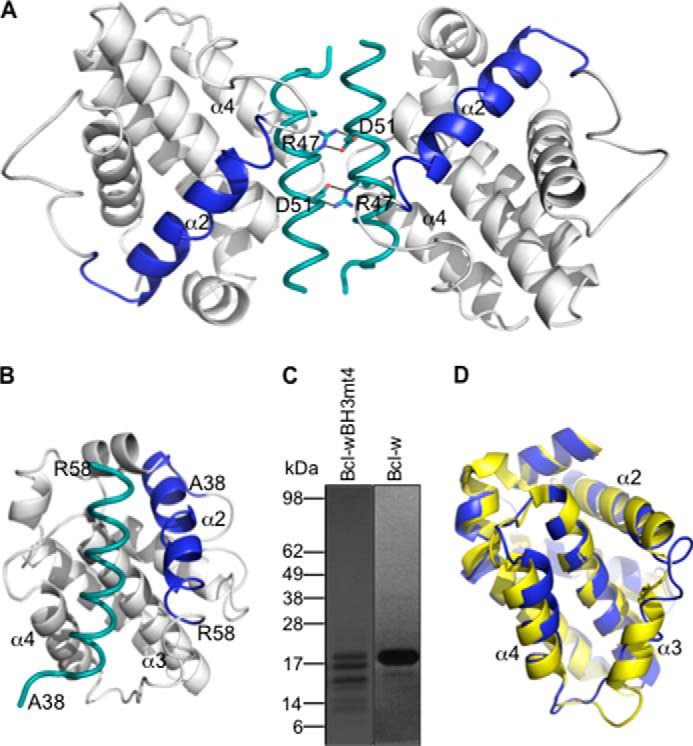
Crystal structure of Bcl-w with a “pro-apoptotic” BH3 domain. A, crystal structure of the Bcl-w dimer formed by reciprocal salt bridges between Arg-47 and Asp-51 on the excised Bcl-w BH3 domains (teal). The position of the excised Bcl-w BH3 domain (residues 38–58) within the intact Bcl-w protein is shown in blue. B, view of the excised BH3 domain (teal) within the canonical binding groove formed by helices α3-α4. C, Coomassie-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel showing that Bcl-w with a mutant BH3 domain is extensively degraded following expression and purification from E. coli, unlike the wild-type protein. D, the overall structure of the Bcl-w BH3 mutant (mauve) is similar to native Bcl-w (yellow; PDB entry 1O0L without the C-terminal “tail” region removed) (37), although the α3 helix is highly disordered and the α2 helix is extended by one extra turn.
