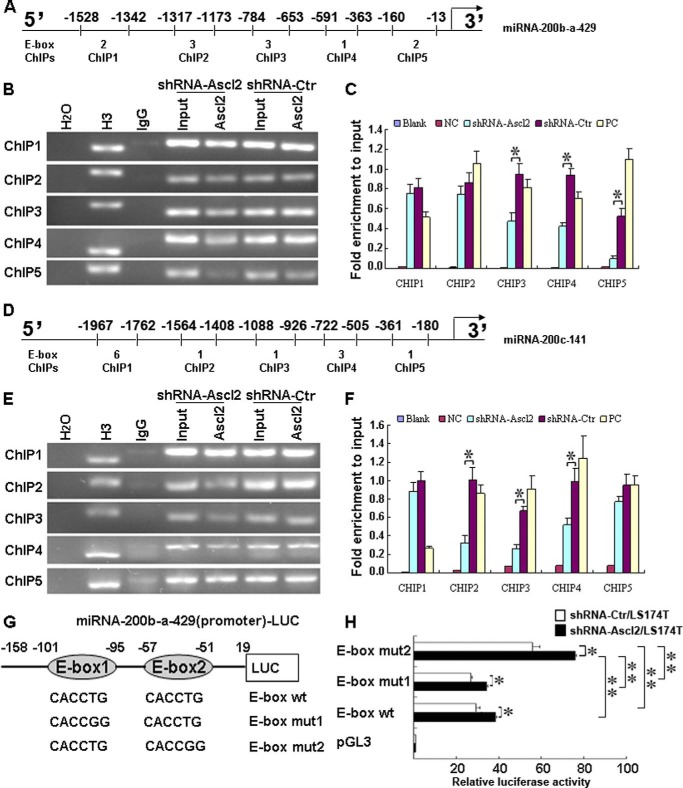
FIGURE 4.
Ascl2 bound to human miR-200b-a-429 or miR-200c-141 promoter in response to Ascl2 knockdown. Chromatin isolated from shRNA-Ascl2/LS174T cells or shRNA-Ctr/LS174T cells was subjected to immunoprecipitation using H2O (negative control), an IgG antibody (negative control), an anti-histone H3 antibody (mAb) (positive control), and a mouse monoclonal IgG against Ascl2 (Millipore, MAB4418). The Input represents 10% of the DNA used in the immunoprecipitation. Five sites in the miR-200b-a-429 and miR-200c-141 promoters with different numbers of E-box elements (ChIP1–5) were tested (A and D). The final DNA extracts were PCR-amplified using primers (B and E). In C and F, the enrichment of the indicated genomic DNA fragments (ChIP1–5), the intergenic control (PC), or unspecific binding (blank and negative control (NC)) was determined relative to the diluted input in three independent experiments. G, schematic representation of the miR-200b-a-429 promoter-Luc construct (−158 to +19), which contains two E-boxes, and its mutants. shRNA-Ascl2/LS174T cells or shRNA-Ctr/LS174T cells were transfected with the miR-200b-a-429 promoter-Luc construct (−158 to +19) and its mutants to identify the sites of transcriptional regulation by Ascl2 (H) (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). Error bars represent S.D.