FIGURE 6.
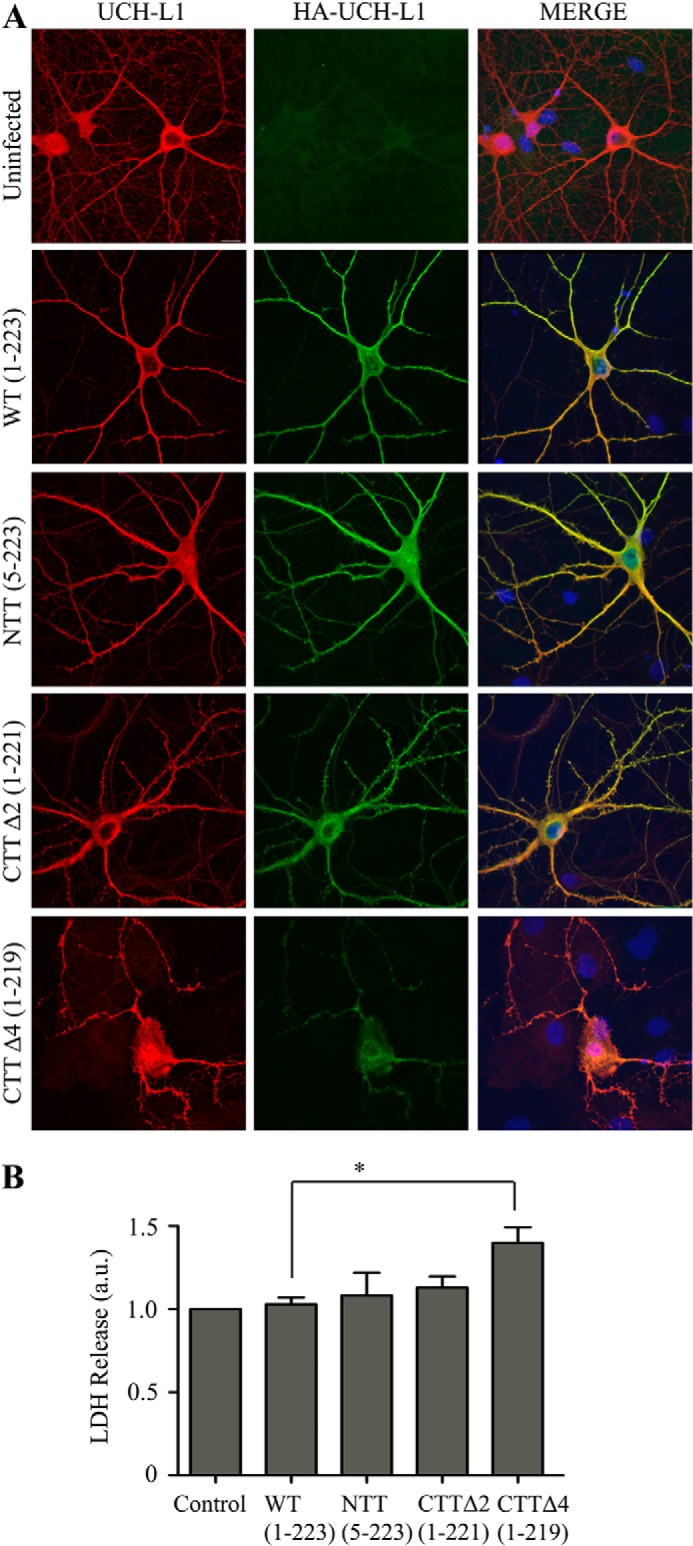
Deletion of the final four residues of UCH-L1 leads to increased cell death. A, deletion of the final four residues leads to altered UCH-L1 distribution. Hippocampal neurons were infected with Sindbis virus expressing the indicated HA-UCH-L1 constructs to assess the distribution of total (endogenous and infected) UCH-L1 and infected HA-UCH-L1. HA-UCH-L1 distribution in WT, N-terminal truncation, and CTTΔ2-infected cells is comparable with endogenous UCH-L1. Infected protein is largely absent from the processes. B, deletion of the final four residues leads to increased cell death. The cell death assay measured the release of lactate dehydrogenase. Infection with Sindbis virus expressing the HA-CTTΔ4 construct caused a significant increase in cell death in cortical neurons compared with HA-WT. Control, uninfected. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance with post hoc Bonferroni test. *, p < 0.05. Control, HA-WT, and HA-CTTΔ4, n = 5; HA-NTT, n = 4; HA-CTTΔ2, n = 3.
