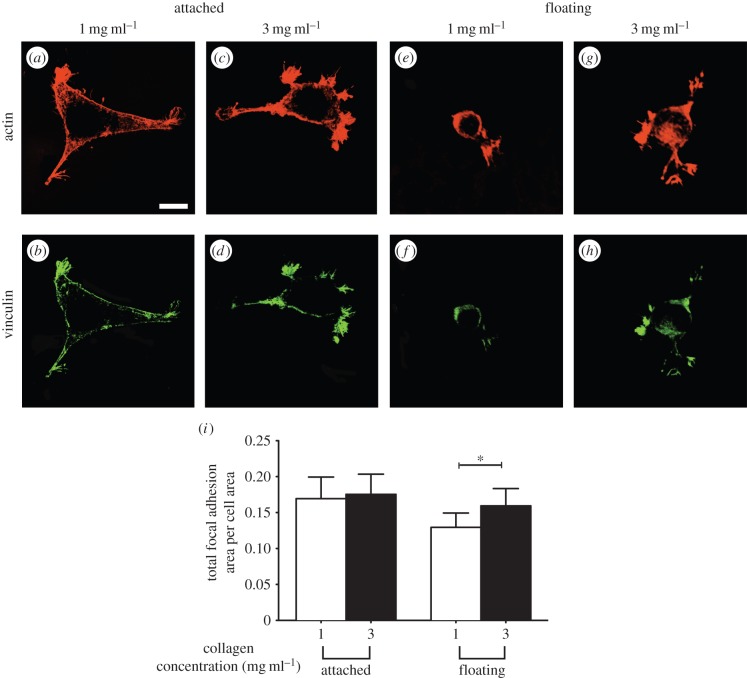
Figure 9.
Impact of the presence of underlying physical boundaries on formation of focal adhesions. Adherent cells to collagen gels of indicated concentration, and physical boundary conditions were fixed and visualized by immunostaining for actin and vinculin. Actin filaments (phalloidin staining) and focal adhesions (vinculin staining) of cells on thin attached gels at collagen concentration of 1 mg ml−1 (a and b, respectively) and 3 mg ml−1 (c and d, respectively). Actin filaments (phalloidin staining) and focal adhesions (vinculin staining) of cells on thin floating gels at collagen concentration of 1 mg ml−1 (e and f, respectively) and 3 mg ml−1 (g and h, respectively). (i) Total focal adhesion area per cell as a function of physical properties and boundary conditions of their collagen matrices. Error bars represent s.d. At least 40 cells per group have been measured. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. p-value was calculated with unpaired Student's t-tests (*p < 0.01). Scale bar, 20 µm. (Online version in colour.)