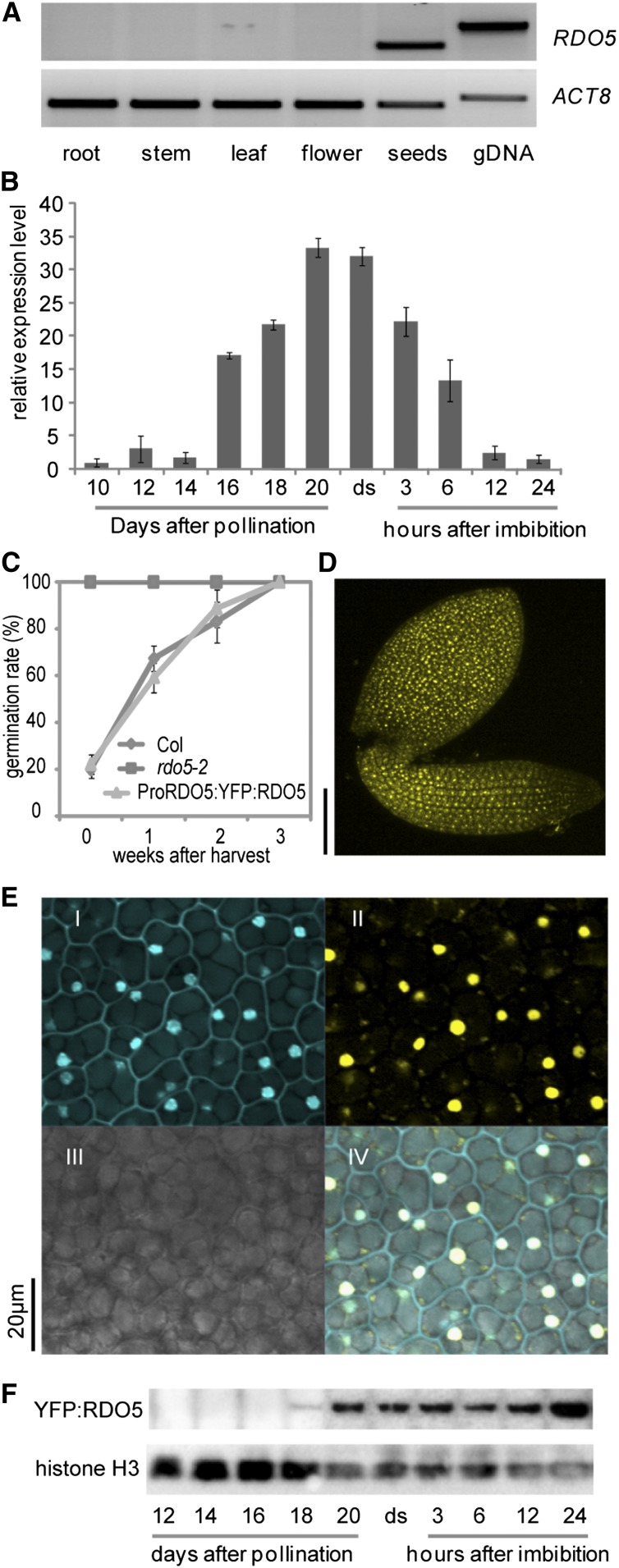
Figure 2.
RDO5 Transcripts Are Seed-Specific and Its Encoded Protein Is Localized in the Nucleus.
(A) RT-PCR analysis of RDO5 transcript levels in various tissues. ACT8 was used as a loading control.
(B) qRT-PCR analysis of RDO5 transcript levels during seed maturation and imbibition. The expression values were normalized using ACT8 as control. n = 3 biological replicates; error bars represent se.
(C) Germination after different periods of dry storage of wild-type Col, rdo5-2, and a transgenic rdo5 line containing the ProRDO5:YFP:RDO5 construct. Shown are averages ± se of six to eight independent batches of seeds for each genotype.
(D) Localization of YFP:RDO5 in an embryo of a freshly harvested seed from a transgenic rdo5 plant containing the ProRDO5:YFP:RDO5 construct. Bar = 100 μm.
(E) Subcellular localization of YFP:RDO5 in embryo cells from a transgenic rdo5-2 seed containing the ProRDO5:YFP:RDO5 construct. I to IV show 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole signal, YFP signal, transmission, and merged images, respectively. Bar = 20 μm.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of YFP:RDO5 protein accumulation in the rdo5-2 complementation line during seed maturation and imbibition. Histone H3 was used as loading control. ds, freshly harvested dry seeds.