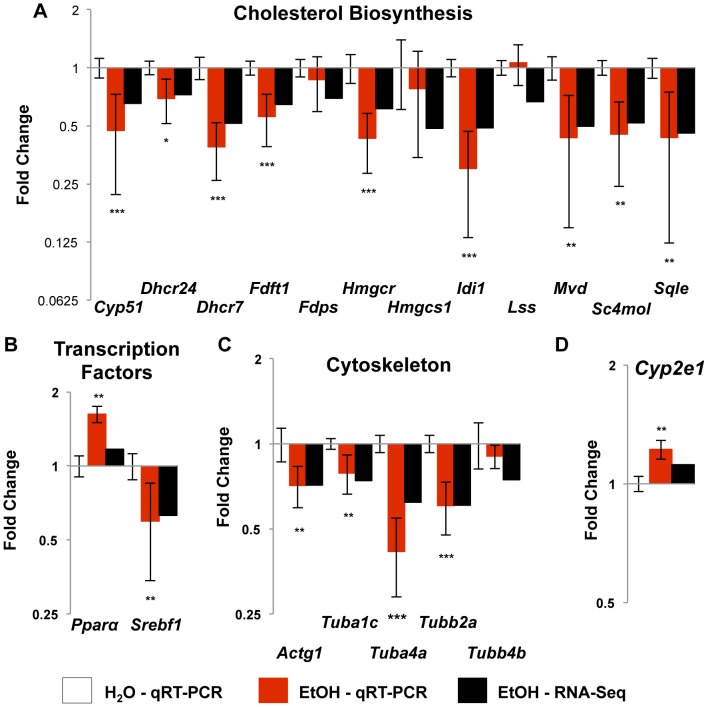
Figure 3. Confirmation of altered expression by qRT-PCR in functional pathway genes.
Taqman-based qRT-PCR was used to confirm the changes in gene expression. These graphs display the fold change (±SEM) of the candidate genes by qRT-PCR (red bars) and RNA-Seq (black bars) analysis for comparison. Numbers are relative to the water treated control rats (set at 1.0). (A) Nine of twelve genes in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway were confirmed. (B) Pparα, a transcription factor that activates genes for cholesterol oxidation was not significantly altered by RNA-Seq analysis, but was significantly up-regulated by qRT-PCR. Srebf1, a transcriptioin factor that activates many genes in the synthesis pathway, was significantly decreased in both analyses. (C) Four cytoskeleton subunit genes were suppressed by RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR. (D) Cyp2e1, a gene induced by chronic high levels of alcohol intake that mediates various alcohol-induced injuries was not induced when measured by RNA-Seq analysis, but was significantly up-regulated by qRT-PCR. * - p-value <0.05, ** - p-value <0.005, *** - p-value <0.0001.