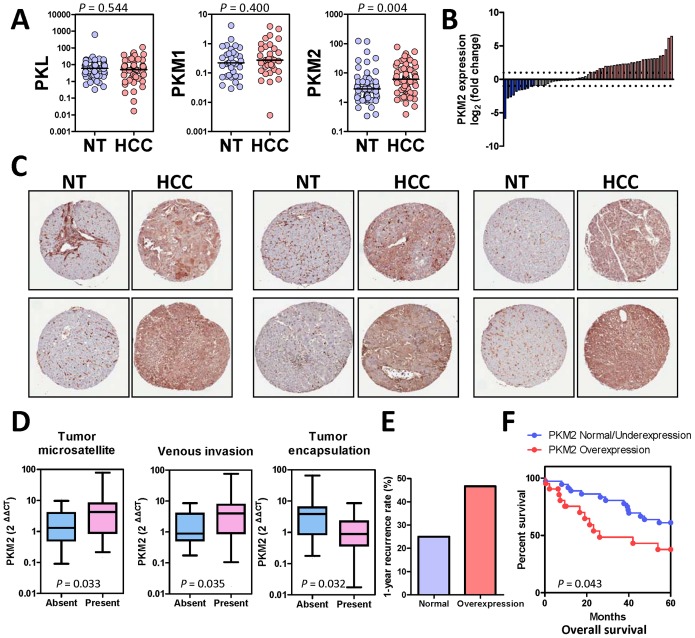
Figure 1. PKM2 expression in human HCC.
(A) mRNA expression of PKL, PKM1, and PKM2 in HCC and NT tissues. Values = 2ΔΔCT, ΔΔCT = (CTPK – CTHPRT) of HCC - (CTPK– CTHPRT) of NT. P values, Wilcoxin signed rank test (B) Waterfall plot shows that, at the mRNA level, PKM2 was up-regulated (HCC/NT2 folds) in 29/60 (48.33%) human HCC samples. (C) Representative pictures of IHC staining with antibody against PKM2 in HCC tissue microarray. PKM2 protein was drastically up-regulated in human HCCs as compared to the paired NT tissues. (D) Mann Whitney test showed that PKM2 over-expression was associated with multiple aggressive clinicopathological features in HCC including the presence of tumor microsatellites, presence of venous invasion, and absence of tumor encapsulation. (E) Over-expression of PKM2 in human HCC was associated with poor prognosis. HCC patients were categorized into two groups: PKM2 over-expression and PKM2 normal/under-expression. PKM2 was considered to be over-expressed when HCC/NT2 folds and was considered to be normal/under-expressed otherwise. HCC patients with PKM2 over-expression had a higher 1-year tumor recurrence rate after surgical resection than HCC patients without PKM2 over-expression, 46.667% Vs 25%. (F) Patients with PKM2 over-expression had lower 5-year overall survival rates after surgical resection. P values were calculated by Kaplan-Meir log rank test.