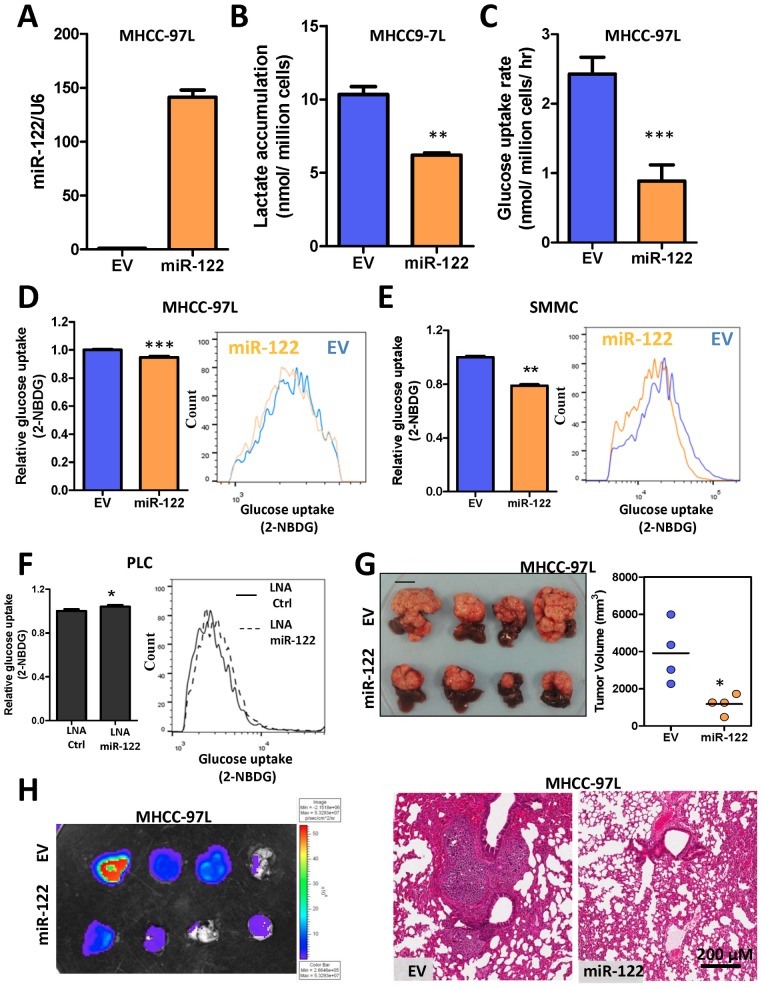
Figure 5. Re-expression of miR-122 suppressed HCC growth through modulating aerobic glycolysis.
(A) miR-122 expression in MHCC-97L cells stably expressing miR-122 precursors. MiR-122 expression was normalized to U6 expression and to empty vector (EV) control. (B) Lactate accumulation was reduced in miR-122 over-expressing MHCC-97L cells. (C) Glucose uptake rate was reduced in miR-122 over-expressing MHCC-97L cells. (D) Glucose uptake in MHCC-97L-EV and –miR-122 cells was confirmed with 2-NBDG staining. (E) Glucose uptake in SMMC-EV and –miR-122 cells was confirmed with 2-NBDG staining. (F) Glucose uptake in PLC/PRF/5 cells transfected with LNA-Ctrl and LNA-miR-122. (G) Left: Orthotopic tumors derived from MHCC-97L-EV and -miR-122 subclones. Right: Tumor volume was measured at the end of the experiment. (H) Bioluminescence (left) and H&E staining (right) in lung tissues from mice implanted with MHCC-97L-EV and –miR-122 subclones. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, *** P<0.001, Student’s t test or paired t test. Scale: 1 cm.