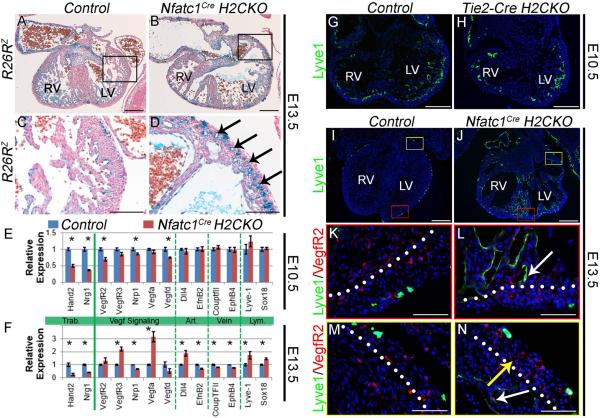
Figure 6. Hand2 controls coronary development and endocardial maturation via regulation of Vegf signaling.
R26RlacZ stained E13.5 hearts (A, B). LV outer curvature (C, D). Nfatc1Cre H2CKOs display hyper-vascularization (arrows in D). qPCR analysis of E10.5 and E13.5 gene expression (n = 4) in Nfatc1Cre H2CKOs (E, F; Asterisks denote significant difference (p≤0.05). Lyve-1 immunostaining in E10.5 Control and Tie2-CreH2CKO hearts (G, H). Lyve-1 immunostaining in E13.5 Control and Nfatc1Cre H2CKO hearts (I–N). In E13.5 control hearts Lyve-1 expression is restricted to endothelial lymphatic precursors (K), while H2CKOs continue to express Lvye-1 within ventricular endocardium (L white arrow). Persistent Lyve-1 expression marks ventricular endocardium (N white arrow) but not coronary endothelium (N yellow arrow). Dotted lines denote the border between compact and trabecular myocardium. Scale bars in A and B represent 250μm, 100μm for C and D, 200μm for G and H, 250μm for I and J, and 50μm for K–N.