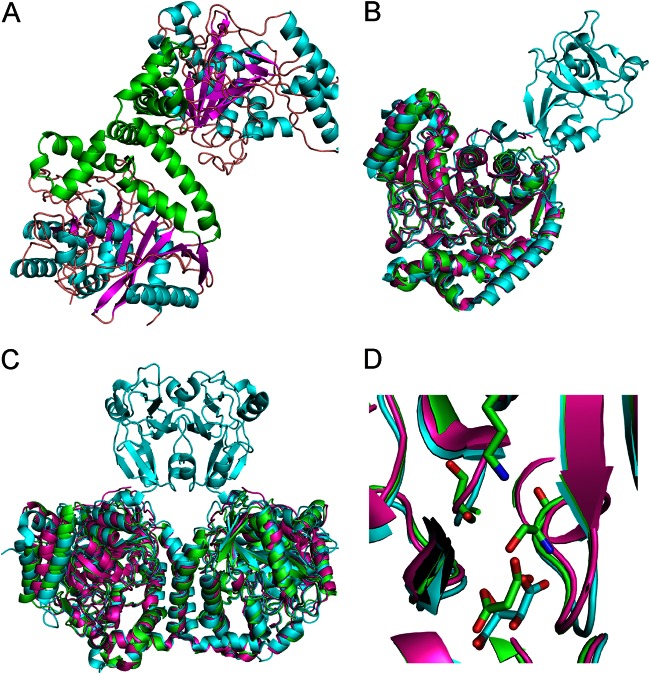
FIG 3.
The AtzF structure and comparison to related structures. (A) A cartoon diagram of the dimer of the AtzF structure with the secondary structure colored by magenta for the beta sheet, cyan for alpha helices, and orange for loop structures. AtzF has two main domains: the catalytic domain and a second all-alpha-helical domain that forms the dimer interface. This has been highlighted by coloring these helices in green. (B) The AtzF structure superposed with structures with PDB accession numbers 4ISS and 4GYS. The structure with PDB accession number 4ISS is colored in cyan and has an extra domain which extends away from the rest of the molecule; AtzF is colored green, and the structure with PDB accession number 4GYS is colored magenta. The structures superpose well, despite limited sequence identity, with RMSD values of 1.3 to 1.6 Å. (C) Comparison of the AtzF dimer and the dimers with PDB accession numbers 4ISS and 4GYS. The figure shows how the dimers are similar and how the dimer with the extra domain (PDB accession number 4ISS) helps the dimer formation for this protein. (D) The catalytic site of these proteins. In two cases we see substrate mimetics bound into the catalytic site: in the case of AtzF we see clear density for malonate, whereas for the structure with PDB accession number 4ISS, there is tartrate.