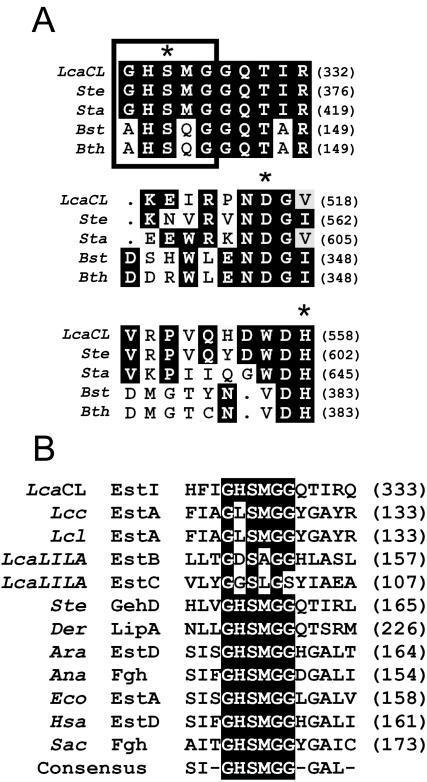
FIG. 3.
(A) Multiple alignment of the possible catalytic triad of L. casei CL96 EstI (LcaCL) (GenBank accession number AY251019) with lipase precursors from S. epidermidis (Ste) (AF090142) and S. aureus (Sta) (AAA26633), an esterase from B. stearothermophilus (Bst) (AF237623), and a tributyrin esterase from G. thermocatenulatus (Bth) (CAA64621). The residues of the catalytic triad are marked with asterisks. (B) Sequence alignment of the active-site consensus motif of EstI (LcaCL) with a tributyrin esterase from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris (Lcc) (AF059739), an esterase from Lactococcus lactis (Lcl) (AF157601), an arylesterase (EstB) from L. casei LILA (LcaLILA) (AF494421), an esterase (EstC) from L. casei LILA (AF506279), a lipase precursor from S. epidermidis (Ste), esterases from D. radiodurans (Der) (AAF09912) and Arabidopsis thaliana (Ara) (AC002510), an FGH from Anabaena azollae (Ana) (AF035558), an esterase from E. coli (Eco) (AAC73458), esterase D (EstD) from Homo sapiens (Hsa) (NP001975), and FGH from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sac) (CAA84054). Highlighted residues are conserved in the majority of sequences aligned.