Figure 3.
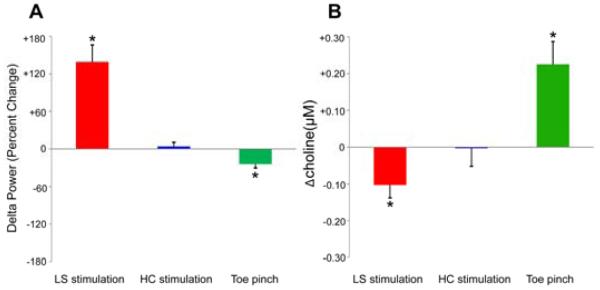
Reciprocal changes in delta power and choline signals with septal stimulation and toe pinch. Group data for orbital frontal cortical changes in LFP delta power and choline levels during electrical stimulation of lateral septum (LS) and hippocampus (HC) or during toe pinch. (A) LFP delta power changes in OFC during electrical stimulation in LS and HC or toe pinch compared to baseline. Stimulation of LS produced a statistically significant increase in cortical delta frequency LFP power, whereas stimulation of hippocampus caused no change in delta frequency LFP power. In addition, the delta frequency LFP power in OFC decreased significantly during toe pinch. Number of animals = 11 (LS stimulation); 6 (HC stimulation); 14 (toe pinch). (B) Mean ictal changes of choline levels in OFC relative to 60 s baseline are shown during LS or HC stimulation along with mean changes during toe pinch. Choline has a statistically significant decrease in OFC during lateral septal stimulation, whereas no significant difference can be detected during stimulation of HC. Toe pinch elicited a significant choline increase in OFC. Number of animals = 11 (LS stimulation); 6 (HC stimulation); 13 (toe pinch). Results are presented as mean (+/- SEM), two-tailed one sample t test Bonferroni corrected, *P < 0.05.
