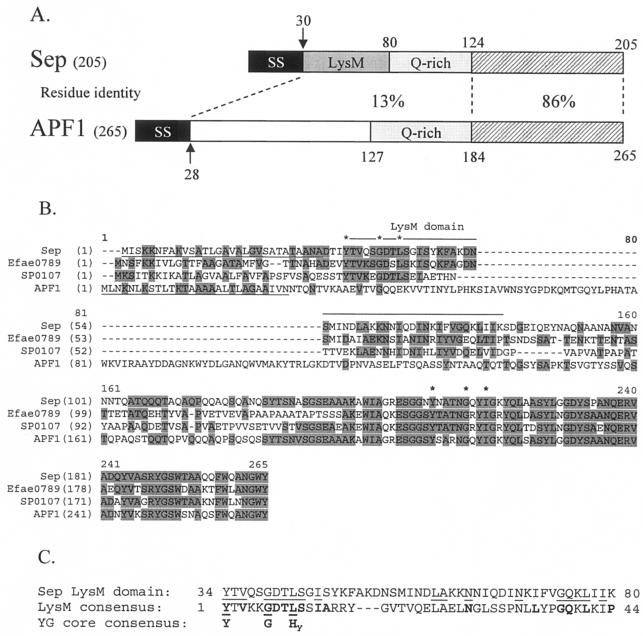
FIG. 2.
(A) Amino acid identity between different regions of Sep from L. fermentum BR11 and APF1 from L. johnsonii ATCC 11506. SS indicates a secretion signal, LysM indicates a LysM domain, Q-rich indicates regions rich in glutamine amino acids, and the hatched boxes indicate the highly homologous carboxy-terminal regions. The arrows indicate cleavage sites of the secretion signals. Note: APF1 does not contain a LysM domain. (B) Multiple alignment of Sep, Efae0789 from E. faecium, SP0107 from S. pneumoniae, and APF1 from L. johnsonii ATCC 11506. Shaded residues indicate identity with the consensus sequence determined using the AlignX program in Vector NTI Suite 6.0. The secretion signals of Sep and APF1 are underlined. The amino-terminal LysM domains found in Sep, Efae0789, and SP0107, but not in APF1, are indicated by a line above the sequence (note: there is one LysM domain for these proteins which extends over the alignment gap). The core residues found in the YG motif in the amino-terminal LysM domains and near the carboxy termini are indicated by asterisks. (C) Alignment of the amino-terminal LysM domain of Sep with the consensus LysM domain pfam01476 (see text) and the core amino acids found in YG domains. Letters in boldface type indicate the consensus sequence amino acids for the LysM and YG core domains. Hy stands for a hydrophobic amino acid. Lines indicate amino acid matches.