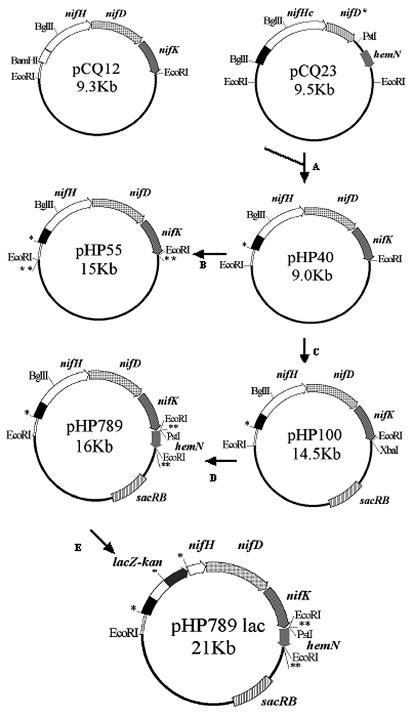
FIG. 1.
Scheme of plasmid construction. (A) pCQ12 was digested with BamHI and BglII; the largest fragment was ligated to a 1.8-kb BglII fragment from pCQ23. The promoter region of nifHDKb (pr b) is represented by an open box, and the promoter region of nifHc (pr c) is represented by a closed box. (B) pHP40 was digested with EcoRI, and the fragment containing pr c nifHcDK was cloned into the EcoRI site of pIC20H, which was then digested with SpeI, and the fragment of interest was cloned into the XbaI site of pTR101. (C) pHP40 was digested with EcoRI, and the 4.5-kb fragment containing pr c nifHcDK was cloned into the EcoRI site of pWS233, generating pHP100 plasmid. (D) pHP100 was digested with XbaI and ligated into a 1.6-kb SpeI fragment containing part of the hemN gene from pCQ23 digested with PstI and EcoRI, obtaining pHP789 plasmid. (E) pHP789 was digested with BglII and ligated to a 5-kb BamHI fragment containing lacZ-kan genes. *, site formed by BamHI-BglII joining; **, site formed by XbaI/SpeI joining; plasmids are not drawn to scale.