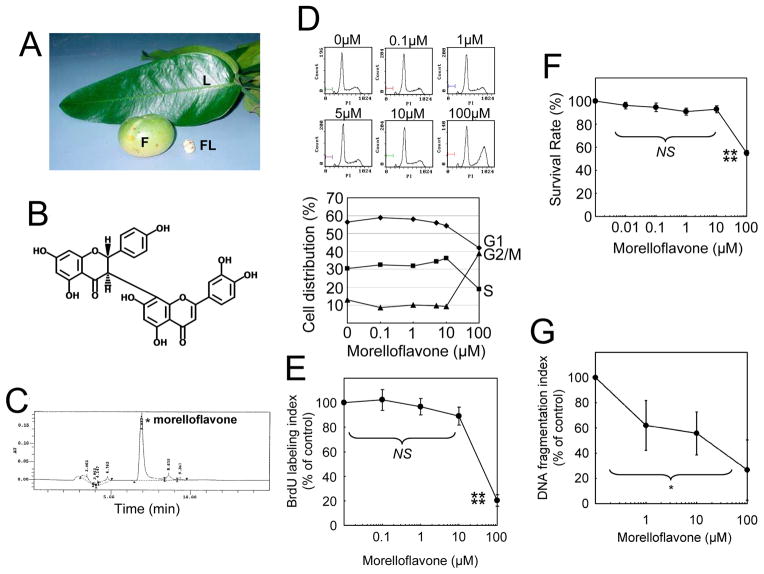
Fig. 1. Morelloflavone does not affect cell cycle progression and causes no cytotoxicity or apoptosis in VSMCs.
(A) Garcinia dulis. L, the leaves; F, fruit; FL, flower. (B) Structure of morelloflavone. Morelloflavone (MW = 556), a biflavonoid, consists of two flavones covalently linked to each other. (C) Purification and characterization of morelloflavone. The current preparation of morelloflavone was purified from the leaves of Garcinia dulis and found to be 93.4% pure as determined by HPLC. (D) Flow cytometric analysis. Cell cycle progression was evaluated by treating VSMCs with various concentrations (0–100 μM) of morelloflavone and subjecting them to flow cytometric analyses (representative data from 3 independent experiments). (E) BrdU assays. The percentage of S-phase cells were determined by treating VSMCs with various concentrations (0–100 μM) of morelloflavone and measuring the uptake of BrdU by these cells (n = 4). Morelloflavone does not affect the percentage of S-phase cells at a concentration equal to or less than 10μM (P = 0.079 by one-way ANOVA on BrdU labelling indices between 0 – 10μM morelloflavone). Morelloflavone, at 100 μM, decreases BrdU labelling indices (****, P < 0.001 for BrdU labelling indices between cells treated with 10 and 100 μM morelloflavone). (F) MTT (3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) VSMC viability assay. Morelloflavone is not cytotoxic to VSMCs at concentrations up to 10 μM (NS [P = 0.071] for MTT survival rate [%] among 0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 μM, by one-way ANOVA; ****, P < 0.001 for MTT survival rate (%) between 10 and 100 μM morelloflavone; n = 4). (G) DNA fragmentation assay. DNA fragmentation indices decreased as morelloflavone concentrations increased (n = 2 each for 0, 1, 10, and 100 μM; *, P = 0.032, by one-way ANOVA). Morelloflavone does not cause apoptosis at concentrations equal to or less than 100 μM.