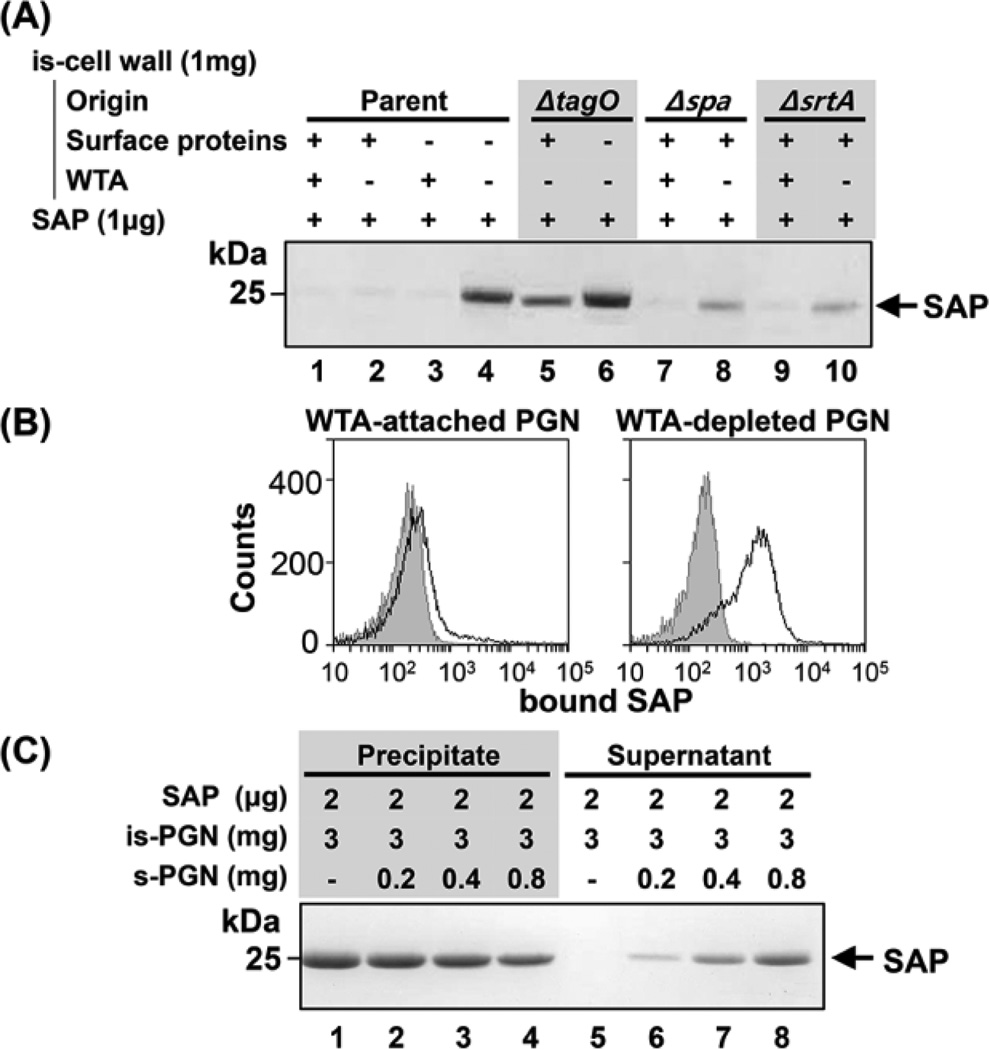
Figure 2. Purified SAP binds specifically to bacterial PGNs.
(A) Insoluble (is)-PGNs were purified from four different S. aureus strains and treated with trypsin or TCA. Next, is-PGN preparations (1 mg) from sortase- or WTA-depleted were incubated with 1 µg SAP for 1 h at 4°C, recovered by centrifugation, and washed. Proteins bound to the is-PGNs were eluted with Tris-buffered saline (TBS, pH 8.0) containing 10 mM EDTA and analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 15% gel under non-reducing conditions. (B) Measurement of the binding between FITC-labeled SAP and WTA-linked or WTA-depleted PGNs using flow cytometry. The curves with gray areas underneath represent cell-only controls. (C) Competitive inhibition experiments; various concentrations of purified soluble (s)-PGN were added to reaction mixtures containing 3 mg of is-PGNs and 2 µg of SAP and incubated for 1 h at 4°C. Is-PGNs were recovered by centrifugation and washed; SAP bound to is-PGNs was eluted in TBS (pH 8.0) containing 10 mM EDTA, and SAP released from is-PGN was recovered by TCA treatment. Samples of SAP bound and released were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 15% gel under non-reducing conditions.