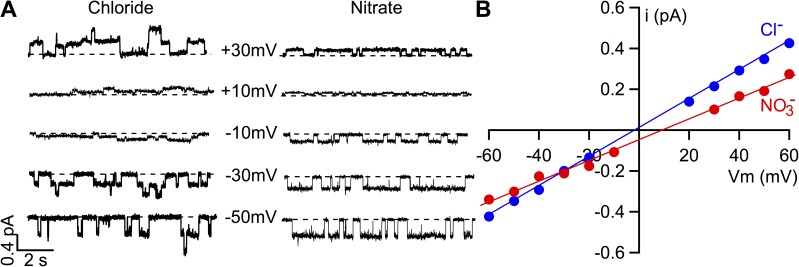
Figure 2.
Comparisons of permeability and conductance of microscopic CFTR currents between Cl− and NO3−. (A) Representative single-channel CFTR current traces at different membrane potentials in the presence of bath Cl− or NO3− containing 2 mM ATP. These single-channel data were obtained from two different patches, and hence the number of channels is not the same. The apparent inconsistent activity in Cl− bath at different voltages is probably caused by partial dephosphorylation of the channel during prolonged recording. (B) Single-channel I-V relationships with bath Cl− or NO3−. The reversal potential in this microscopic I-V curve is shifted to a positive voltage when bath Cl− is replaced by NO3−. In contrast to the difference in macroscopic CFTR conductance shown in Fig. 1 B, single-channel conductance in bath NO3− is lower than that in Cl−.