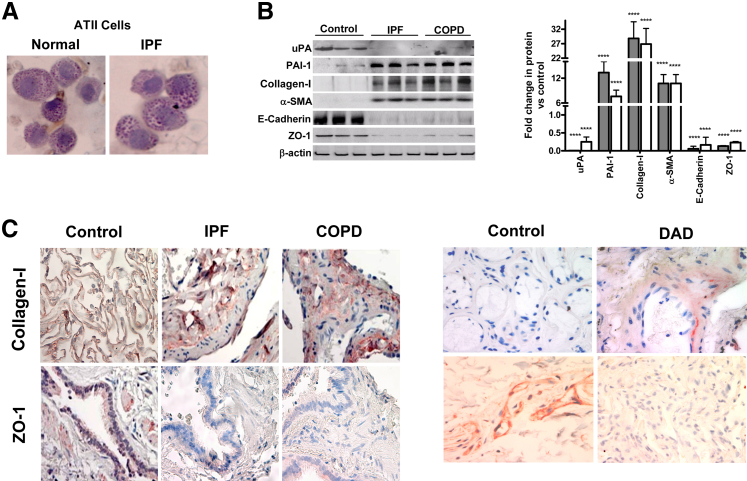
Figure 1.
Altered expressions of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) are associated with alveolar type II (ATII) cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lungs. A: ATII cells isolated from lung explants were stained for inclusion bodies using lithium carbonate to assess the purity of the cell preparation. B: ATII cells isolated from patients (n = 3) with IPF (gray bars) or COPD (white bars) and from healthy donors. The lysates were analyzed for changes in the expression of uPA, PAI-1, collagen-I, α-SMA, E-cadherin, ZO-1, and β-actin. The fold changes in densities of individual bands are presented as a bar graph after normalization against the corresponding densities of β-actin antigens present in each sample. C: Paraffin-embedded sections from lung tissues of patients with IPF or COPD or diffused alveolar damage (DAD) and healthy donors were subjected to IHC analysis for changes in collagen-I and ZO-1 antigen levels in situ. Representative photomicrograph (from n = 5) is shown. ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.