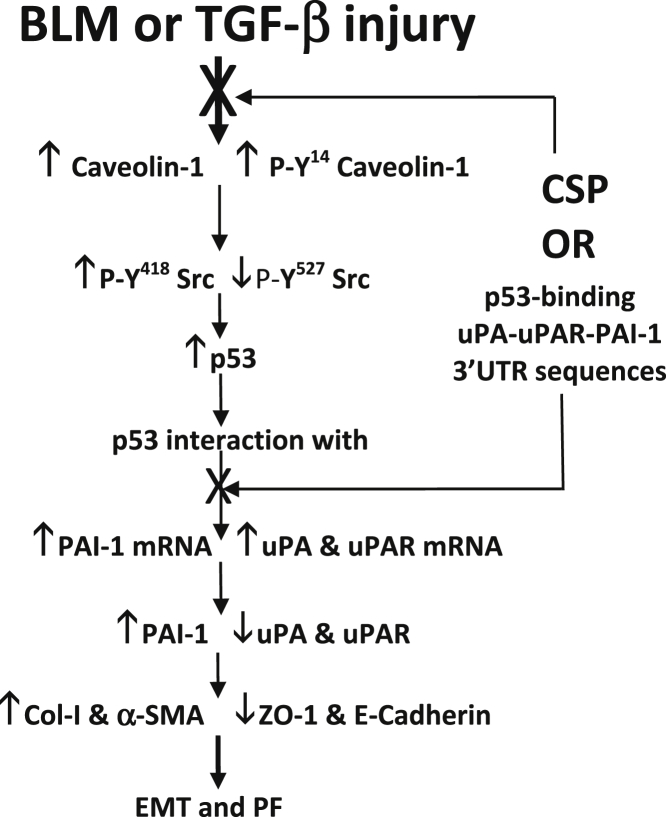
Figure 7.
Regulation of ATII cell epithelial–mesenchymal transitions (EMT) and pulmonary fibrosis (PF) through p53–uPA–fibrinolytic system cross talk. Increased expression and phosphorylation of caveolin-1 by activated Src kinases augments p53 expression in ATII cells during fibrosing lung injury. p53 in turn binds to urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), uPA plasma membrane receptor (uPAR), and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) mRNAs leading to suppression of uPA and uPAR, and increased PAI-1 expression.49–51 This results in enhanced ATII cell EMT and development of PF. Inhibition of p53 interaction with endogenous uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 mRNA in ATII cells either by inhibiting p53 expression using CSP or competitive inhibition through overexpression of p53-binding 3′-UTR sequences of uPA, uPA, and PAI-1 mRNA restores uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 expression and mitigates ATII cell EMT and development of PF after fibrosing lung injury.