Figure 2.
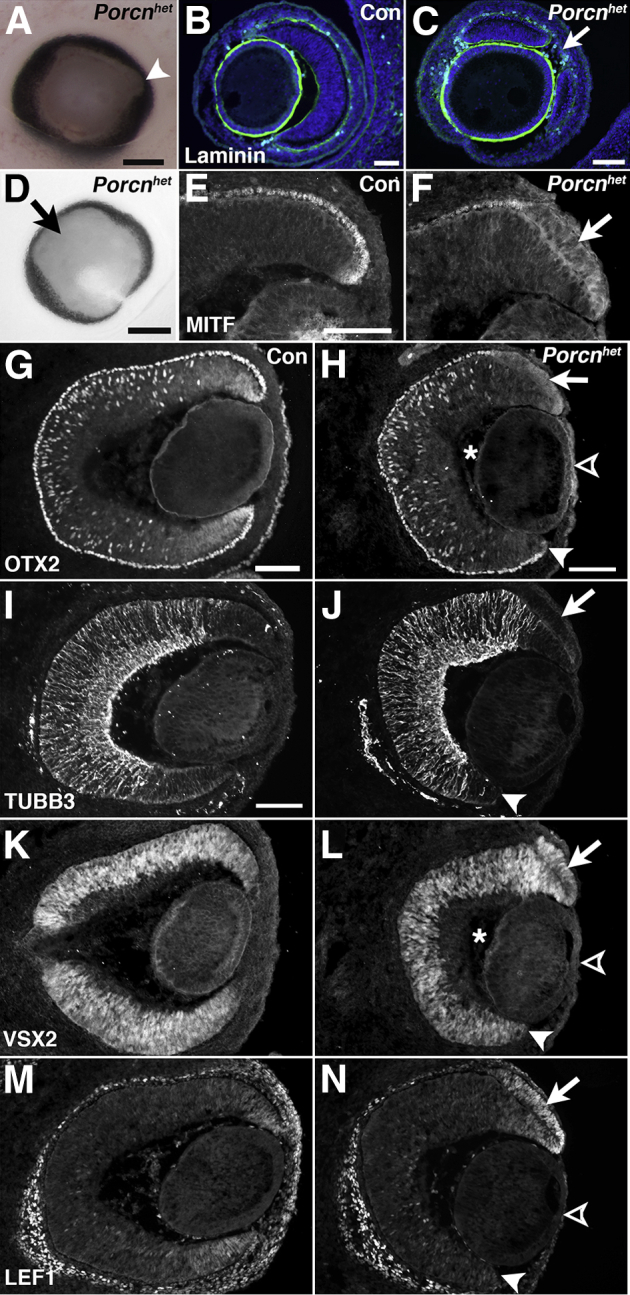
Porcnhet embryos exhibit pigment defects in the optic cup periphery at E13.5. A:Porcnhet eyes exhibit patches of depigmentation, often found temporally (arrowhead) (genotype: PorcnΔ/lox). B: Sagittal view of the ocular periphery shows continuous, basal laminin expression surrounding the lens and the retina and RPE in WT embryo. C: In Porcnhet embryos, unpigmented patches arise from tissue gaps evident by interrupted laminin expression (arrow) (same eye as in A). D: Colobomatous Porcnhet eye with circumferential decrease in pigment (arrow) (genotype: PorcnΔ/lox;Six3-Cre). E: Coronal view of expression of the RPE-specific protein MITF in WT dorsal RPE. F: In Porcnhet embryos, MITF expression is decreased in the RPE of the optic cup periphery (arrow) (same eye as in D). G: Coronal view of OTX2 expression in WT eye. H: OTX2 expression is slightly decreased in the dorsal RPE of Porcnhet embryos (arrow; same eye as in D). I: Expression of the retina-specific marker TUBB3 in WT retina. J: In Porcnhet eyes, TUBB3 is normally expressed in the retina and absent in the dorsal RPE periphery (arrow) (same eye as in D). K: Coronal expression of the retina-specific transcription factor VSX2 in WT retina. L: VSX2 is ectopically up-regulated in the dorsal RPE of Porcnhet embryos (arrow) (same eye as in D). M: In WT embryos at E13.5, LEF1 is expressed in the periphery of the retina and RPE, and in periocular mesenchyme. N: In Porcnhet embryos, LEF1 expression in the ventral optic cup (arrowhead) and in corneal mesenchyme (open arrowhead) is absent but robustly up-regulated in the dorsal RPE (arrow; same eye as in D). H, J, L, and N: Note the shortening of the ventral optic cup (arrowhead), reduction of the vitreous (asterisks), and thinning of the cornea (open arrowhead) in Porcnhet embryonic eyes. Scale bars: 200 μm (A and D); 100 μm (B, C, E, G, H, and I).
