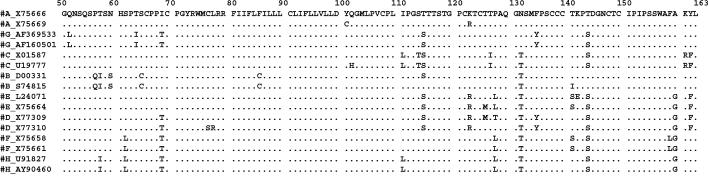
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the HBsAg coding region (amino acids 50 to 163) corresponding to the region amplified for genotyping. GenBank accession number sequence X75666 is shown in detail. For each known HBV genotype, two sequences are shown, and only amino acids differing from X75666 are indicated. Dots indicate that the same amino acid was observed in the sequence. Mutations specific for HBV subtypes: 122 (K = d, R = y), 160 (K = w, R = r), 127 (L = w4), and 140 (S = w4). Mutations related to resistance to HBIg, anti-HBs monoclonal antibody, or vaccination: 107 (Y), 110 (V), 111 (T), 114 (R), 115 (K or S), 116 (S), 117 (R), 118 (A, V, or S), 120 (E, T, S, or N insertion), 121 (T or R inser-tion), 122 (NT insertion or RA insertion), 123 (N or A or NSTGPCTT insertion), 124 (R or Y), 125 (A), 126 (S, N, or A), 127 (S or T), 129 (H), 130 (R or N), 131 (S or I), 132 (P), 133 (T, L, or I), 134 (L, I, S, or N), 135 (S), 137 (Y), 138 (Y or S), 140 (R, I, and P), 141 (E), 142 (S), 143 (W, R, M, or L), 144 (H, N, A, or E), 145 (R, K, or A), 146 (S), 147 (R), 148 (I), 149 (R or W), 154 (T or W), 155 (Y or P), 156 (L), and 157 (R).