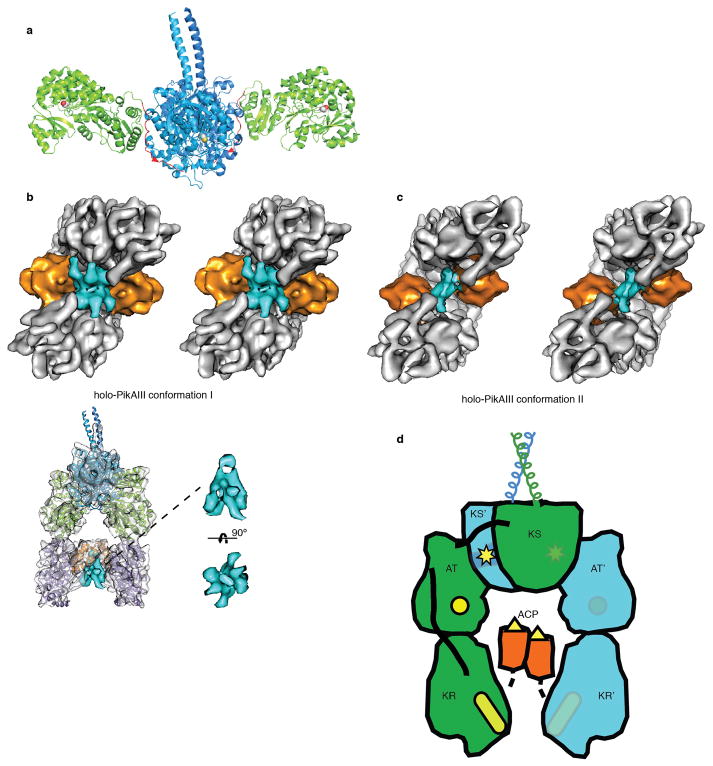
Extended Data Figure 6.
PikAIII domain organization and connectivity. a, Crystal structure of excised DEBS module 5 KS-AT di-domain7. KS (blue, yellow active site) and AT (green with red active site) domains interact differently than in the full module (Fig. 2), and the post-AT linker (red) lies on the surface of the KS domain. b, Localization of post-ACP5 dimerization helices. top: Stereo view of holo-PikAIII conformer I with the density ascribed to the post-ACP5 dimerization helices (rendered in cyan) observed between the ACP5 domains (orange). bottom: Overview of localization and enlarged cut-out densities of post-ACP5 dimerization helices (cyan) in holo-PikAIII conformer I. c, Stereo view of holo-PikAIII conformer II with the density ascribed to the post-ACP5 dimerization helices (rendered in cyan) observed between the ACP5 domains (orange). d, Proposed connectivity of domains in PikAIII determined by distances between domain termini and linker lengths. The catalytic domains are colored (green or blue) according to the assigned polypeptide chain. The AT interacts with the KS of the opposite monomer whereas the AT-KR interaction is within the monomer. Active site locations are indicated in yellow.