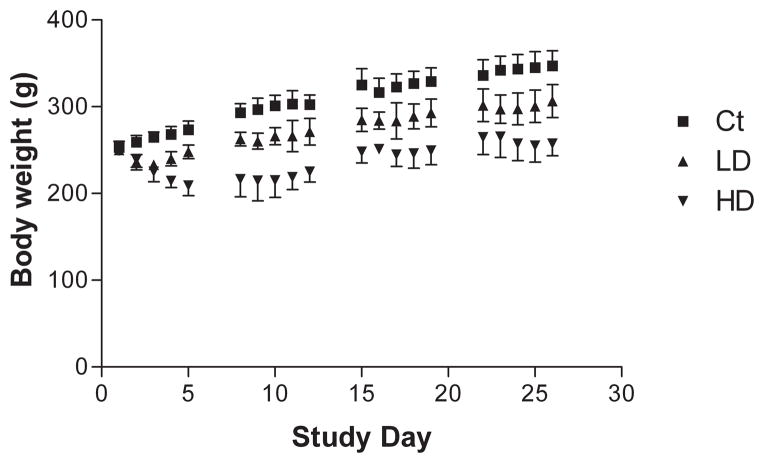
Figure 1.
Daily intraperitoneal injections of MnCl2 results in reduced weight gain in Mn-treated animals. Rats were weighed daily prior to dose administration and weights were averaged for each group. Exposure to MnCl2 induced significant changes in body weights in a dose-dependent manner. A steady increase in average body weights of control rats (square) was observed throughout the study. Animals in the low (triangle) and high (inverted triangle) dose groups showed an initial decrease in body weight but began to gain weight after three and five days, respectively. For the remainder of the study, rats in the dose groups continued to gain weight, but average weights were significantly decreased compared with controls. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and Tukey’s post hoc test (n = 5). Error bars indicate SD. Ct: control; LD: low dose at 6 mg/kg; HD: high dose at 15 mg/kg.