Fig. 1.
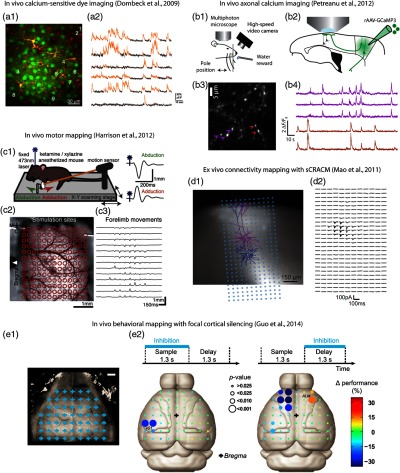
Neurophotonics techniques for investigating neuronal activity and connectivity in motor cortex, and cortical involvement in sensorimotor processing. (a) In vivo calcium-sensitive dye imaging of activity in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in mouse motor cortex. A synthetic calcium-sensitive dye was bulk-loaded into motor cortex, resulting in labeling of layer 2/3 neurons (a1), and two-photon microscopy was used to image calcium transients, representing action potentials, across many neurons in the same field of view (a2). Reproduced with permission from Ref. 21. (b) In vivo axonal calcium imaging. Mice were trained to perform a whisking behavioral task during head fixation (b1). Axons of vibrissal motor cortex (vM1) neurons were labeled with a genetically encoded calcium indicator (rAAV-GCaMP3), and their axons projecting to vibrissal somatosensory cortex (vS1) were imaged with two-photon microscopy [(b2) and (b3)] to detect calcium transients as the mouse performed the motor task (b4). Images from K. Svoboda, modified from Ref. 33. (c) In vivo motor mapping. Mice expressing ChR2 in layer 5B neurons in motor cortex were placed on an apparatus for laser-stimulating the motor cortex while monitoring forelimb movements with a motion sensor (c1). By sequentially stimulating across a grid over the motor cortex (c2), a map of the forelimb movements was obtained (c3). Reproduced with permission from Ref. 34. (d) Ex vivo connectivity mapping. Recordings were made from vM1 neurons in layer 5A (magenta) and 5B (blue) and a photostimulus grid was oriented to span their dendritic arbors (d1). By photostimulating across the array of sites to excite ChR2-expressing presynaptic terminals of axons originating from S1, a subcellular-resolution map was obtained revealing the dendritic sites of long-range input from S1 to these L5A neurons in M1 (d2). Reproduced with permission from Ref. 35. (e) In vivo behavioral mapping. In mice in which cortical interneurons express ChR2, cortical sites were focally inhibited during a sensorimotor task (e1). Scale bar, 1 mm. This approach identified roles for somatosensory cortex (e2, left) and anterior lateral motor cortex (e2, right) during different phases of the behavioral task. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 36.
