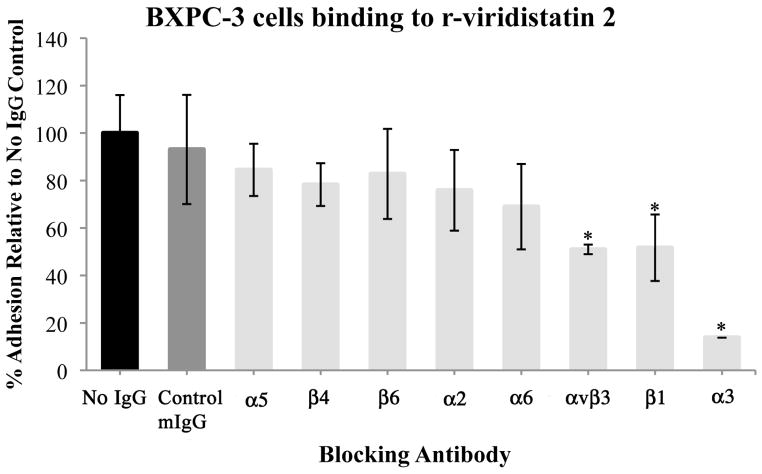
Figure 2.

Identification of the integrin specificity of r-viridistatin 2 (A) and r-mojastin 1 (B). BXPC-3 cells were preincubated with PBS (no IgG), control murine IgG (mIgG) or specific anti-integrin antibodies, and then added to a 96 well-plate coated with r-disintegrins (40 μg/mL), followed by a quantitative inhibition adhesion assay as described in methods section. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D for percentage adhesion relative to the no IgG control (* p < 0.05). Inhibition assay with immobilized monoclonal antibodies to α3 and β1(C). BXPC-3 cells were preincubated with PBS (control), or recombinant disintegrins (5μM), and then added to a 96 well-plate coated with monoclonal antibodies to α3 and β1 (40 μg/mL), followed by a quantitative inhibition adhesion assay as described in methods section. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D for percentage adhesion relative to the control (* p < 0.05). Negative control of adhesion was performed with the plate coated with murine IgG (mIgG) at 40 μg/mL.