Figure 2.
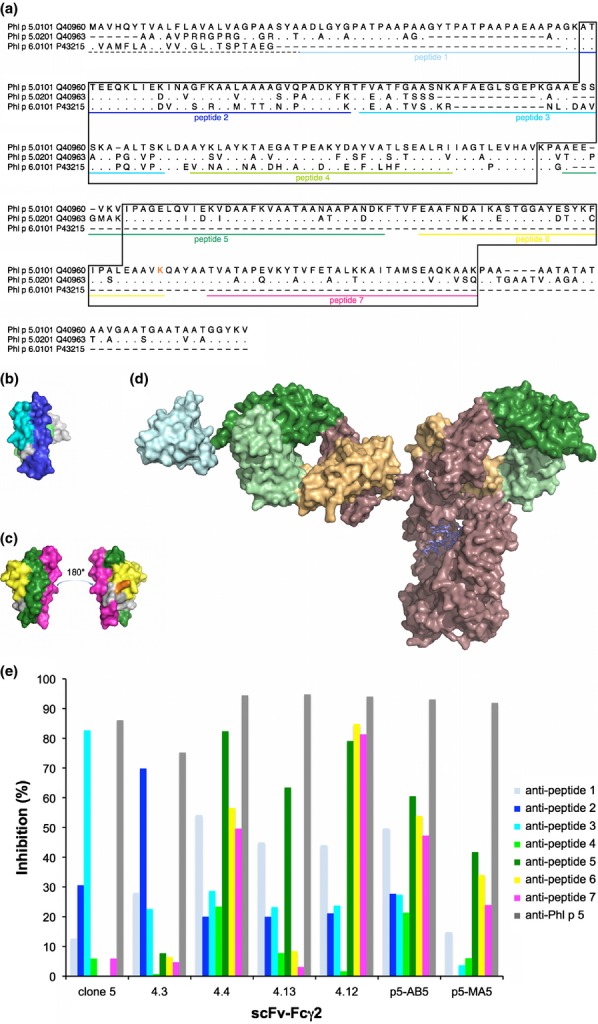
Localization of epitopes on Phl p 5. The sequences (including the signal sequences (dashed line)) of the two isoallergens of Phl p 5 and the related allergen Phl p 6 (GenBank accession numbers are indicated) are aligned (a). Residues identical to those found in Phl p 5.0101 are indicated by dots; missing residues are indicated by dashes. The parts of Phl p 6 and the C-terminal domain of Phl p 5 that are visible in 3D-structures (PDB: 1NLX and 1L3P, respectively) are boxed. Sequences of peptides derived from the Phl p 5.0101 sequence that were used for epitope mapping are underlined in colour. Residue K246 (incorporated in peptide 6) of Phl p 5.0101 is printed in orange. The position of peptides are highlighted in the structures of Phl p 6 (PDB: 1NLX) (b) and the C-terminal domain of Phl p 5.0201 (PDB: 1L3P) (c). A schematic illustration of the size difference between an antibody, in this case an IgG (PDB: 1HZH) and the C-terminal domain of Phl p 5 (PDB: 1L3P; cyan) is shown (d). Antibody variable and constant domains are coloured green and brown with sequences that belong to heavy and light chains shown in dark and pale colour, respectively. (e) Percentages inhibition (y-axis) of binding of scFv–Fcγ2 (x-axis) to Phl p 5 by rabbit anti-peptide and anti-Phl p 5 anti-sera.
