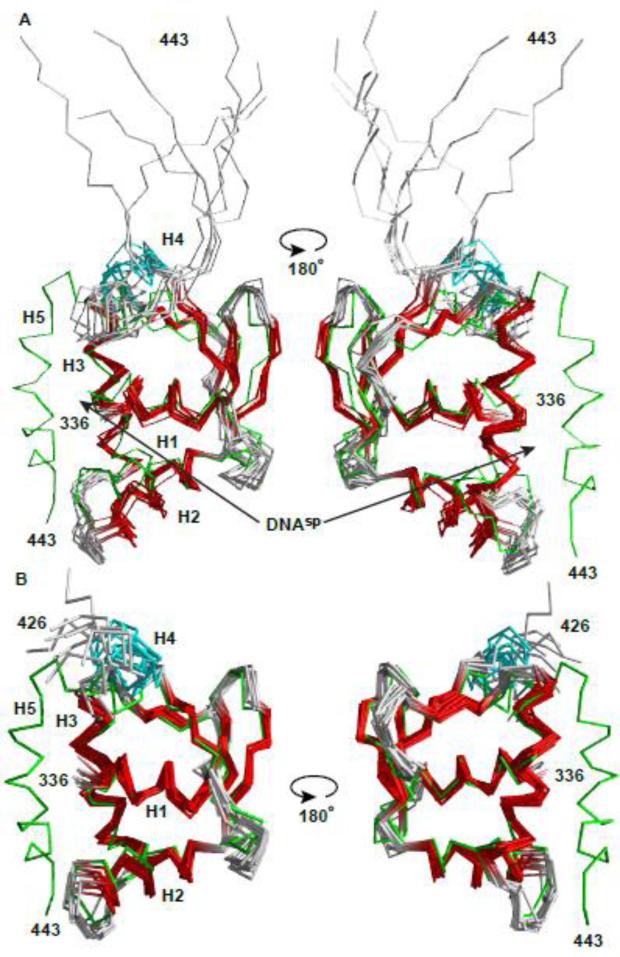
Fig. 3. Structural ensembles of free and bound ETV6 are similar except for the unfolding of helix H5.
The NMR-derived structural ensembles of (A) the ETV6D446–DNAsp complex (ETS domain helices and strands, red; CID helix H4, cyan) and (B) uninhibited ETV6R426 align closely to the lowest energy structure of inhibited ETV6R458 (green).16 CID helix H5, which blocks the DNA-binding interface of ETV6R458, is absent in ETV6R426 and unfolded in the ETV6D446-DNAsp complex. Although present in the latter complex, DNAsp was not included in the structure calculations. The N-terminal Gly-Ser-His-Met and unstructured residues (329-335 and 444-446) are not shown for clarity. Arrows point to the DNA-binding interface along helix H3.