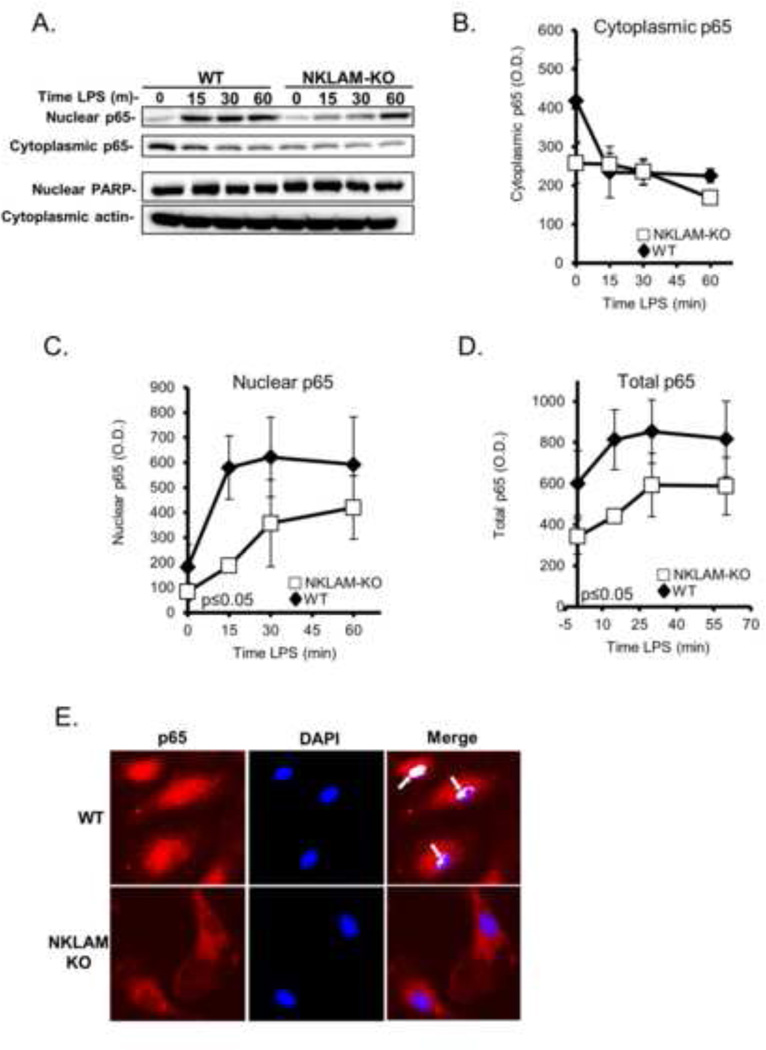
Figure 5. NFκB p65 expression and nuclear translocation in WT and NKLAM-KO BMDM.
A–D) WT and NKLAM-KO BMDM were treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for the times indicated. Isolated cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions were immunoblotted for p65. Immunoblotting for PARP (nuclear lysates) and actin (cytoplasmic lysates) was done to show purity of the fractions and equivalent protein loading. A) Immunoblots represent one of 3 identical experiments. B–D) Densitometric analysis of p65 in cytoplasmic, nuclear and total cellular lysates from WT and NKLAM-KO macrophages treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for the times indicated. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. of three experiments; p ≤ 0.05, one-way ANOVA, comparing response of WT and NKLAM-KO BMDM. E) Monolayers of WT and NKLAM-KO BMDM were treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 15 min and then immunostained for p65 (red). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows denote areas of p65/DNA colocalization (white) as defined by the ImageJ Colocalization Finder plugin.