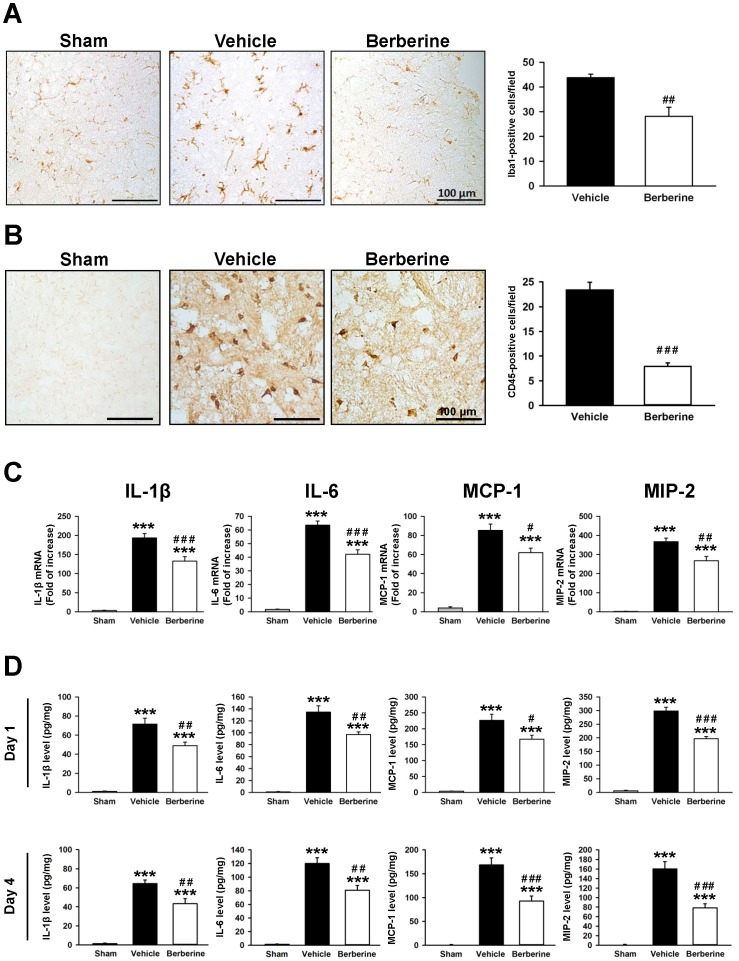
Figure 5. Post-injury berberine treatment reduced microglial activation, macrophage infiltration and expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Representative (A) anti-ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1)-stained and (B) CD45-stained brain sections from a sham-injured control, a vehicle-treated, and a 10 mg·kg−1 berberine-treated mouse at 1 day post-TBI. Cell count analysis shows that berberine-treated mice had significantly fewer Iba1-positive and CD45- positive cells than vehicle-treated mice in the cortical contusion margin at 1 day post-TBI. The number of Iba1-positive and CD45-cells is expressed as the mean number per field of view (0.8 mm2). Scale bar, 100 µm. Values are presented as means ± SEM; ## P<0.01 vs. the vehicle group as determined by the Student's t-test (n = 6 mice/group for Iba1 and CD45 staining). (C) Bar graphs demonstrating interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-2) mRNA expression as assessed by Taqman reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in the ipsilateral cortices of sham control, vehicle-treated, and 10 mg·kg−1 berberine-treated mice at 6 h post-injury. Berberine significantly attenuated IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1 and MIP-2 mRNA expression compared with vehicle-treated mice. (D) Bar graphs of IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and MIP-2 protein concentrations, as assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in the ipsilateral cortices of sham control, vehicle-treated, and 10 mg·kg−1 berberine-treated mice at 1 and 4 days post-injury. Berberine-treated mice exhibited significantly reduced IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and MIP-2 protein levels compared with vehicle-treated mice at both 1 day 4 days. Values are presented as means ± SEM; ***P<0.001 vs. the sham control; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs. the vehicle group as determined by one-way ANOVA (n = 5–7 mice/group for ELISA and n = 7 mice/group for RT-PCR).