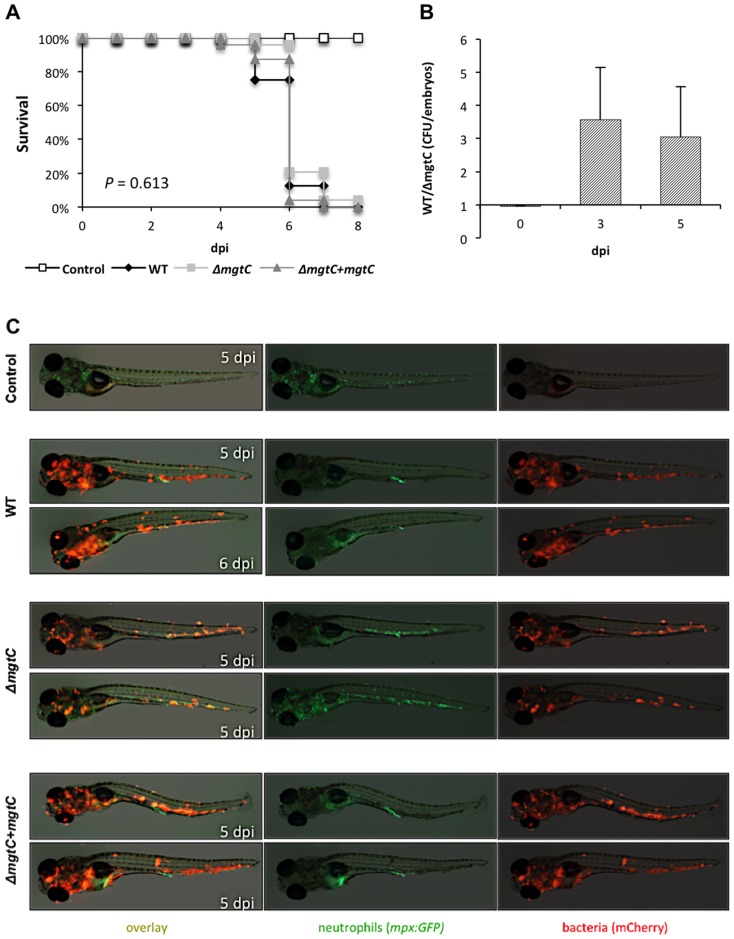
Figure 4. Intravenous infection of zebrafish with the Mma mgtC mutant.
(A) Survival of 30 hpf embryos intravenously infected with 150–200 CFU of wild-type M. marinum, ΔmgtC mutant or complemented strain compared to non-injected controls (n = 24). Results are from a representative experiment (infection with 133 CFU for wild-type, 142 CFU for mgtC mutant and 205 CFU for complemented strain) out of three independent experiments. (B) Ratio of whole embryo bacterial counts between Mma M and mgtC mutant strain-infected embryos at 0, 3 and 5 dpi. A ratio of 1 indicates equal CFU values. A ratio >1 indicates that WT CFU are higher than mgtC mutant CFU. Results are expressed as mean CFU per embryo+SD from four independent experiments (0 and 5 dpi) or two independent experiments (3 dpi). The mild difference between mutant and wild-type strains is not statistically significant (Student Test). (C) Visualization of neutrophils in mpx:GFP infected larvae at late stages of infection (one day before embryo's death). Neutrophils fluoresce in green while mcherry-expressing bacteria fluoresce in red. Neutropenia occurs in wild-type and complemented strains but not in the mgtC mutant.